:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TikTok-vs-YouTube-a42ac0c72a4f4b1d9da8b7ae85b4205e.jpg)
New Have You Ever Used the Path Blur Effect in Your Photos? This Article Will Address How to Use Path Blur in Photoshop to Generate Appealing Results Accurately

Have You Ever Used the Path Blur Effect in Your Photos? This Article Will Address How to Use Path Blur in Photoshop to Generate Appealing Results Accurately
There are different kinds of blur effects that redefine the movement and intensity of an image. By applying a suitable blur effect, you can increase the visual appeal of your still photo by emphasizing a certain motion. Path blur is one of the trending motion blur effects that people use to enhance their photos instantly. Through this article, you can learn how to use path blur in Photoshop conveniently.
Part 1: What is Path Blur and How Does It Work?
Path blur is a kind of motion blur that highlights a motion and speed in a certain direction. It helps to create a sense of movement by adjusting the blur intensity and central point. If you want to display a stimulating motion in an image, path blur can assist you in this regard.
Path blur works by adjusting two variables: Speed and Taper. By adjusting the speed slider, you can specify the amount of path blur. In addition to speed, you can adjust the taper value accordingly to determine the blur trail.

This effect can instantly add new dimensions to your captured photo. For instance, if you have captured a photo of a racing car, you can add a path blur effect to give a sense of speed to it. You can easily find this special effect in Adobe Photoshop. By using the selection tools, you can effectively add a path blur effect to your image in the selected area. To know more about path blur in Photoshop, continue reading this article.
Part 2: How to Use Path Blur in Photoshop?
Photoshop is undoubtedly the most commonly used tool to edit pictures with great configuration options. After uploading the image, you can quickly transform it by adding new effects, filters, and layers. You can retouch your photography efficiently through this tool by increasing the quality of pictures. Moreover, the clean user interface of Photoshop allows you to utilize the advanced functions without any interruptions.
Are you ready to use Photoshop path blur? Read this part of the article to find out two interesting ways to create a path blur effect in the images.
Add Dynamic Effect to Your Static Images
Step1 Open Photoshop and import the desired picture. Once done, go to the “Layers” section and copy the background layer. For this, press “Ctrl + J” in Windows and “Command + J” for MacBook.

Step2 Now proceed to the “Filter” section and locate the option “Blur Gallery”. From there, choose the “Path Blur” option. Now you would be able to see an arrow on your screen. Using this arrow, you can specify the path blur motion. Drag and close the arrow where you want to show the speed. Also, set a higher value for the speed given on the right side. Once done, hit the “OK” button.

Create a Long Exposure Picture
Step1 Navigate to the Adobe Photoshop tool and begin by uploading a picture. Afterward, go to the “Filter” tab and select “Convert for Small Filters.”

Step2 Now go to the “Filter” tab again and choose the “Blur Gallery” option. From there, select the “Path Blur” option. Now adjust the displayed arrow in a particular direction to decide the starting and endpoint of the path blur. Moreover, modify the “Speed” slider according to your choice.

Step3 After dragging the arrow in a particular direction, a blue dot will appear at the center. Press the “Delete” button to eliminate that point. Now select the endpoint of the arrow and change its blur shape.

Step4 Utilize the noise section to add a grainy effect in the blurred area. Once done, click on the “OK” button. Now select the masking tool to select the area in your picture. Afterward, choose the “Smart Mask” filter and then navigate to the “Fill” option given in the “Edit” section.

Step5 In the fill menu, choose the color “Black.” Now go to the “Select” section and click “Deselect.” To soften the whole look, you can go to the “Properties” panel and adjust the “Feather” properties.

Step6 Now add the first layer and choose the option “Convert for Smart Filters.” Again, go to the “Filter” section, select “Blur Gallery,” and uncheck the option called “Edit Blur Screen.”

Step7 Now increase the length of the arrow and press “Ctrl + Click” for Windows or “Command + Click” for Mac to reposition the path. You can also add a curve to the arrow. Enhance the speed from the right panel and uncheck the option of “Center Blur.” You can increase the taper value to make the blur gradually trail off. Add a grainy filter for more enhancements.

Bonus Tips – The Alternative to Photoshop to Create Motion Blur Effect
Many users find the interface of Adobe Photoshop intimidating or challenging to operate. If you want an alternative to Photoshop, the best choice you can make is to use Wondershare Filmora . For beginners, this tool adds built-in presets that are professionally made.
Free Download For Win 7 or later(64-bit)
Free Download For macOS 10.14 or later
It offers more than 900 effects that you can use to add new dimensions to your photos and videos. Moreover, it provides fast processing speed for photo and video editing to help you achieve your goals conveniently.
Steps to Produce Motion Blur Effect in Filmora
If you are a beginner and want to create a motion blur effect, then use the steps mentioned below:
Step1 Add the Image to Timeline
After launching Filmora, select “Create New Project” and import the desired picture. After dragging it to the timeline, you have to split it to proceed.

Step2 Choose the Background Blur
To split, choose the starting and ending point in the clip where you want to add the motion blur effect. Once done, go to the “Effects” tab and search for the “Background Blur” effect section. Pick and apply the desired blur filter to the split section of the video.

Step3 Apply the Transition
Once you have added the motion blur effect, you can check the results from the preview window. You can also apply the “Dissolve” transition from the “Transitions” tab to generate a smooth result.

Conclusion
If you want to display a sense of speed and movement in the picture, you can add a path blur effect. It’s one of the types of motion blur effects that many people use in their pictures to add a dynamic element. By reading this article, you have learned how to add path blur in Photoshop through simple means. Moreover, you can also explore the tool Filmora to create a motion blur effect in the photos effortlessly.
Free Download For macOS 10.14 or later
It offers more than 900 effects that you can use to add new dimensions to your photos and videos. Moreover, it provides fast processing speed for photo and video editing to help you achieve your goals conveniently.
Steps to Produce Motion Blur Effect in Filmora
If you are a beginner and want to create a motion blur effect, then use the steps mentioned below:
Step1 Add the Image to Timeline
After launching Filmora, select “Create New Project” and import the desired picture. After dragging it to the timeline, you have to split it to proceed.

Step2 Choose the Background Blur
To split, choose the starting and ending point in the clip where you want to add the motion blur effect. Once done, go to the “Effects” tab and search for the “Background Blur” effect section. Pick and apply the desired blur filter to the split section of the video.

Step3 Apply the Transition
Once you have added the motion blur effect, you can check the results from the preview window. You can also apply the “Dissolve” transition from the “Transitions” tab to generate a smooth result.

Conclusion
If you want to display a sense of speed and movement in the picture, you can add a path blur effect. It’s one of the types of motion blur effects that many people use in their pictures to add a dynamic element. By reading this article, you have learned how to add path blur in Photoshop through simple means. Moreover, you can also explore the tool Filmora to create a motion blur effect in the photos effortlessly.
How to Add Miniature Effect in Video with Filmora
Want to add selective blur to make everything look smaller? Don’t have any idea how to focus on specific mini-things? Then don’t worry! In this article, you’ll get a step-by-step process to add miniature effects to your video. At the end of the process, you’ll have cinematic shots. Then start with us now! Scroll more to get pro tips!
What Is a Miniature Effect?

But first, let’s learn the logic of making the miniature effect. As many video editing pros present on Tiktok, the miniature effect is a fun way to brighten up your photography or video shots. For example, when taking a video or a time-lapse of a landscape, we always have a bigger depth of field, so most objects in the frame are in focus.
However, when we film a miniature model, the depth of field is shallow. So, we only see some objects in focus, and the rest is blurry. This visual trick makes our brain believe that the big landscape we’re seeing is actually a tiny model.
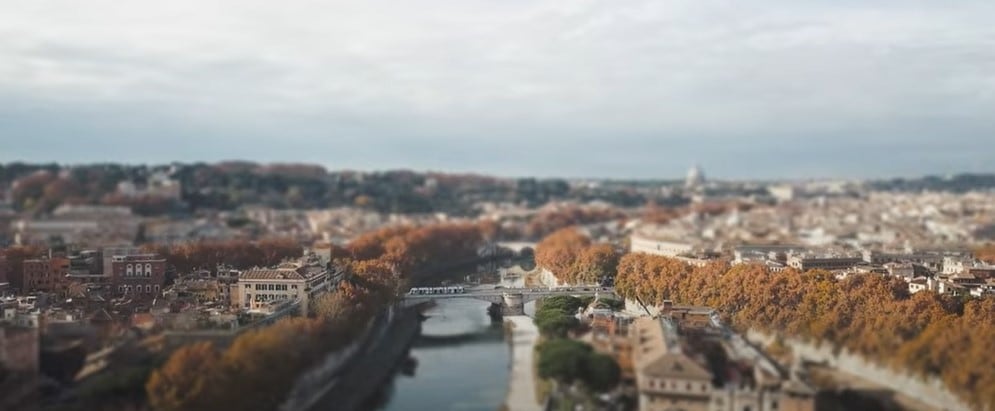

To create a miniature look, we can use specific effects to fake a shallow depth of field, and then the landscape view will look like a tiny model. While some keys to notice before making the miniature effect are:
- It utilizes selective blur to make things appear like small
- The miniature effect works best for footage filmed from a high angle.
- The tiny effect is usually used in drone footage, time lapses, or landscape photography.
Are you all set to add miniature effects to your video and make film-like shots? Then scroll more and get the step-by-step process.
How to Make a Miniature effect?
You are excited to add a miniature effect, and enjoy the rest! Without any further delay, follow the below instructions and get results!
Step1 Download the Wondershare Filmora
- First of all, you have to download the Wondershare Filmora .
- It’s packed with new features and effects plugins that make editing more filmy and fun!
![]()
Note: filmora has a unique “stock media” option that enables us to use all these elements and more to boost our videos!
Step2 Choose any stock footage
If you don’t have good-quality footage, but want to boost your video, here is how. You can get the miniature effect without a big format view camera or specialized lens.
- Open Filmora and select any stock footage in Wondershare Filmora.
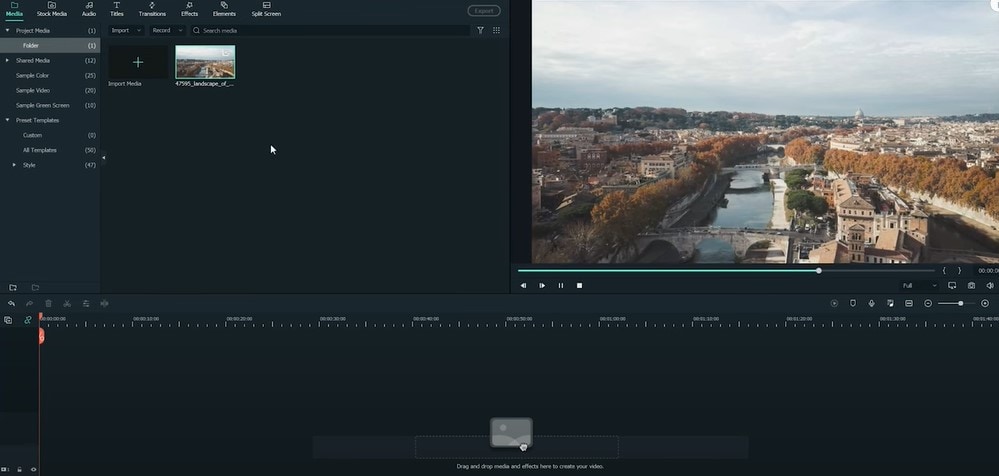
Move to the stock media folder on the above bar in the Wondershare Filmora. Or you can look towards the left window, where you will see the sample videos tab.
- Click on the sample videos tab, and a new window will appear on the library screen.
Here you will see almost more than 20 videos. So, instead of using the actual recorded footage, we’ll make do with what we have by default. After selecting and adding the stock footage of your choice. Then you have to follow the below process:
- First, hold the Stock Footage as shown in the folder section.
- Then Drag and Drop it to the timeline section for further editing.
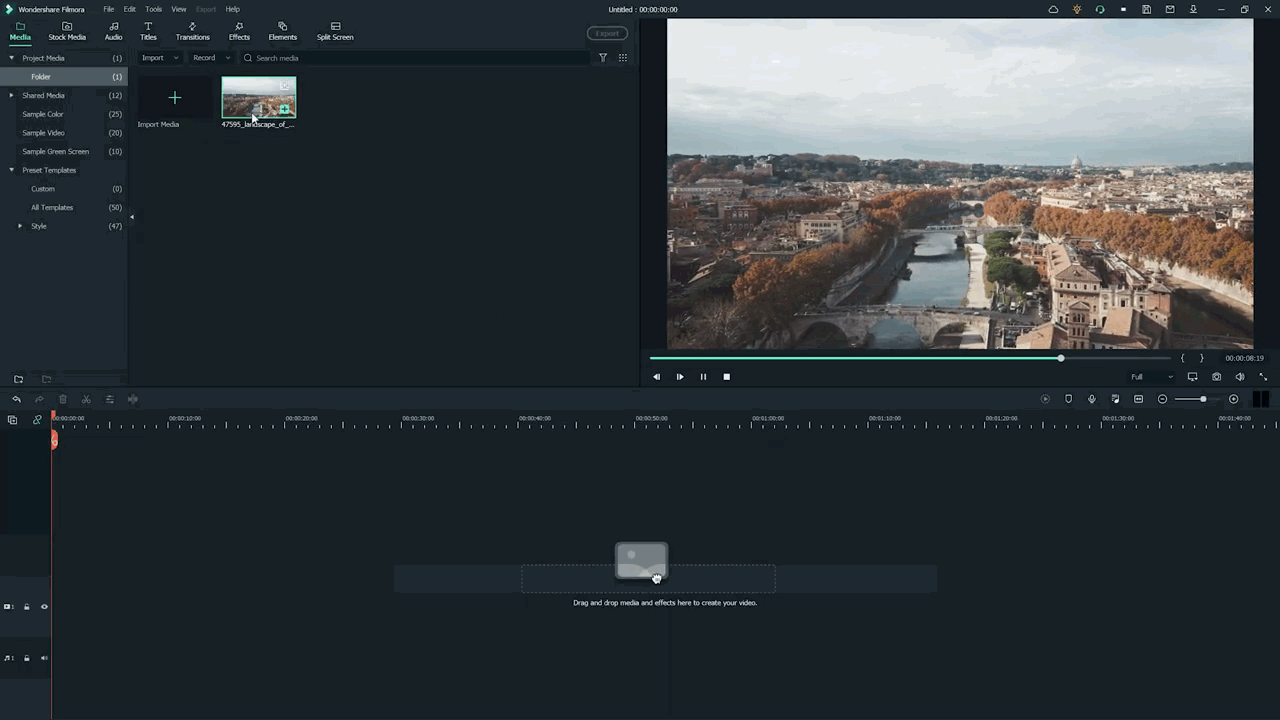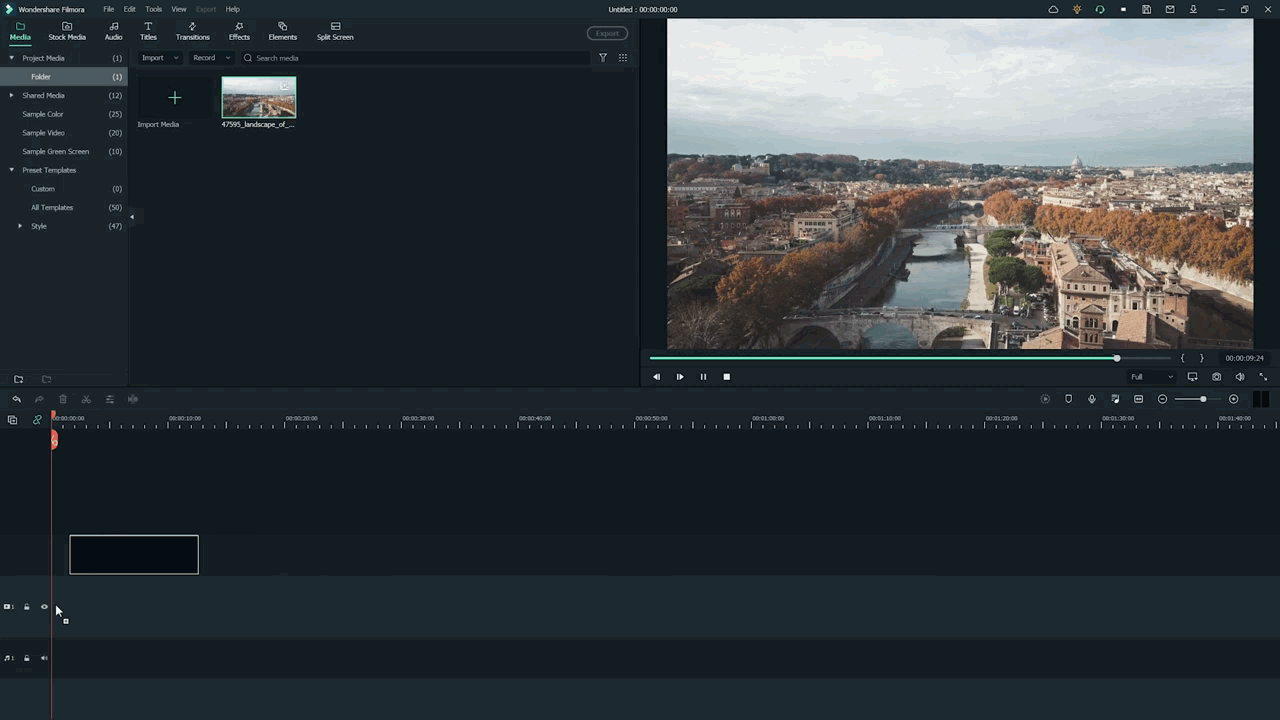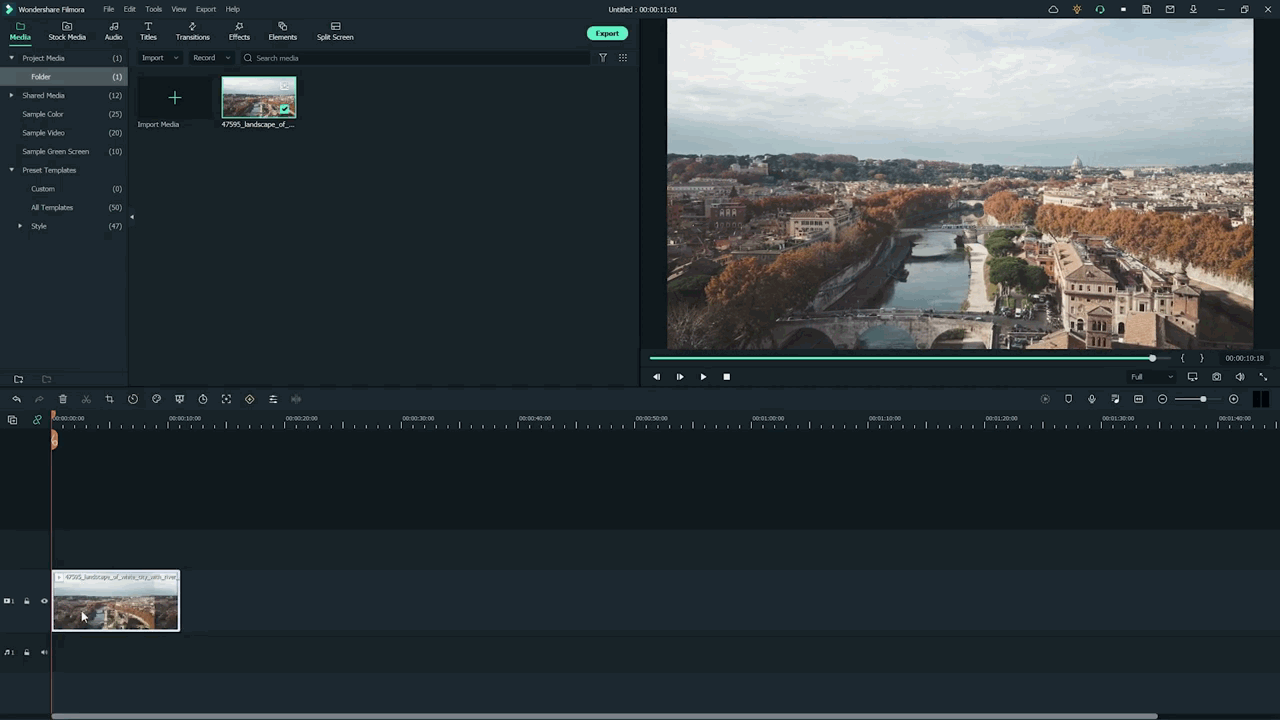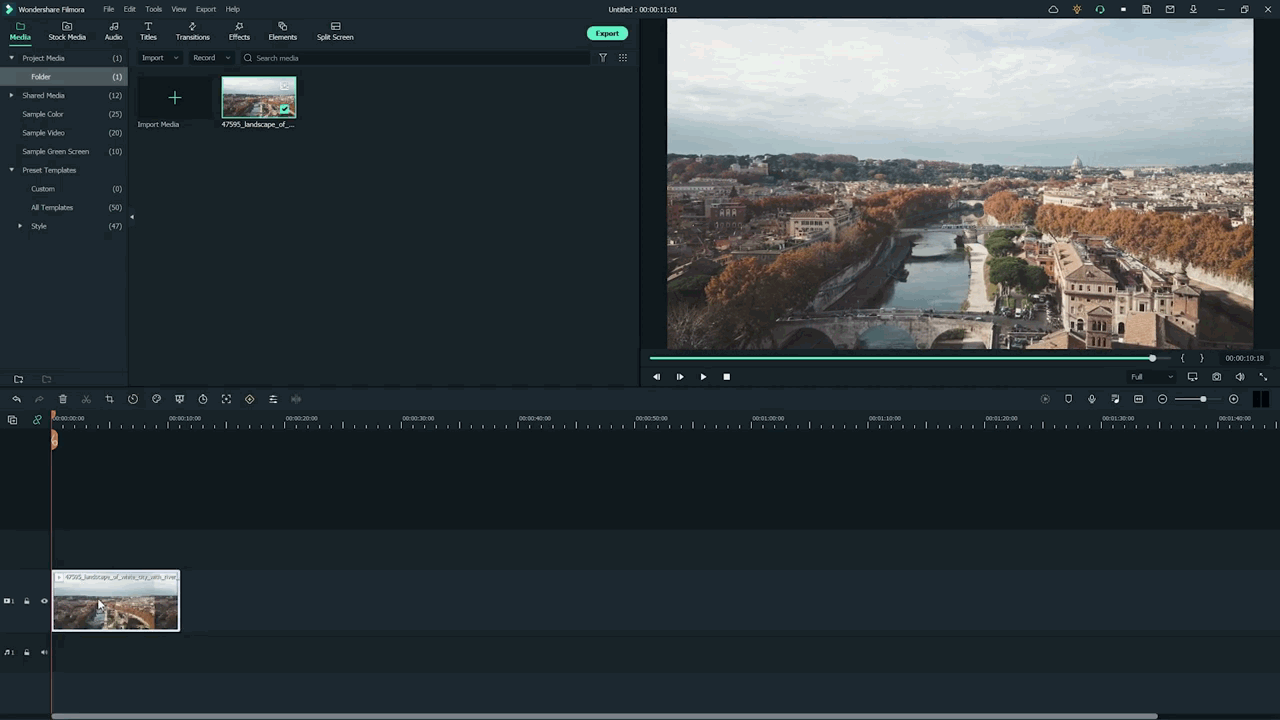
Who will get Stock Media?
Want to get stock media? You can only have access to the stock media library if you already buy the license of Wondershare Filmora.
- The latest version has an unlimited stock library.
- After purchasing any plan, you can access Stock Media (Unsplash, Giphy, Pixabay, Pixel).
Step3 Head to the effect panel
As we are working on miniature effects, what do we need first? First, we ensure that we have a Blur effect on the video.
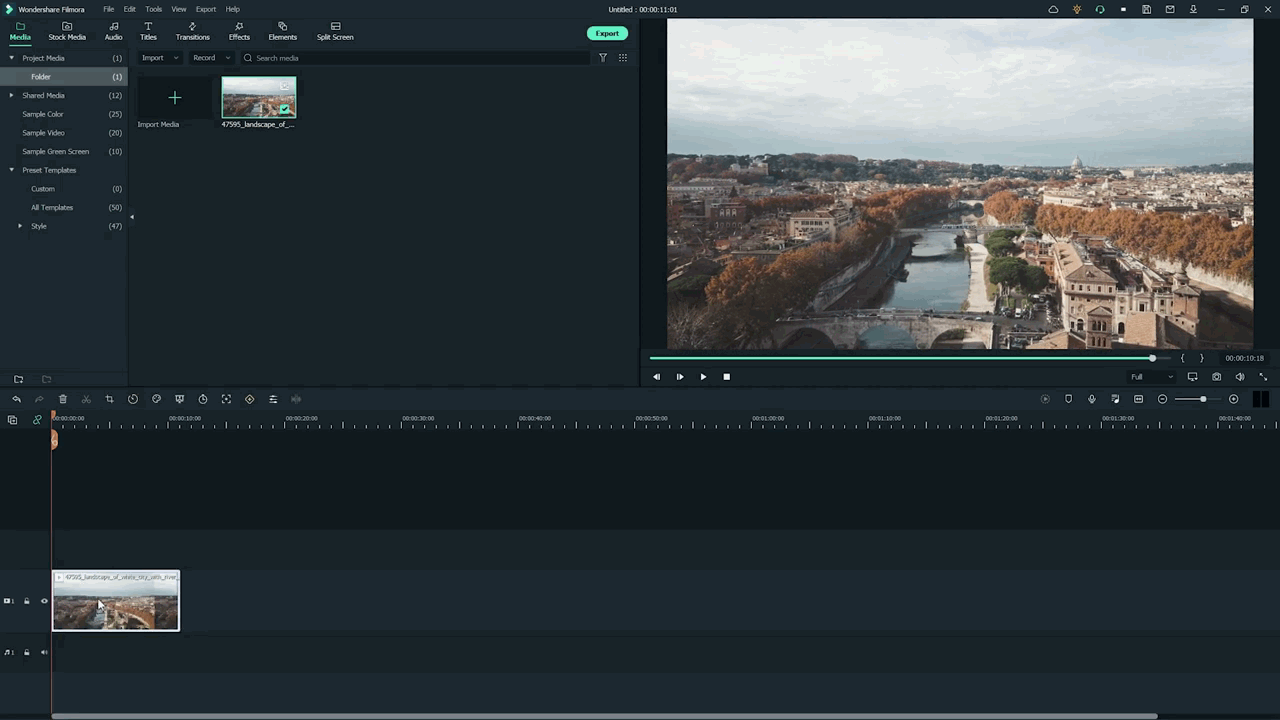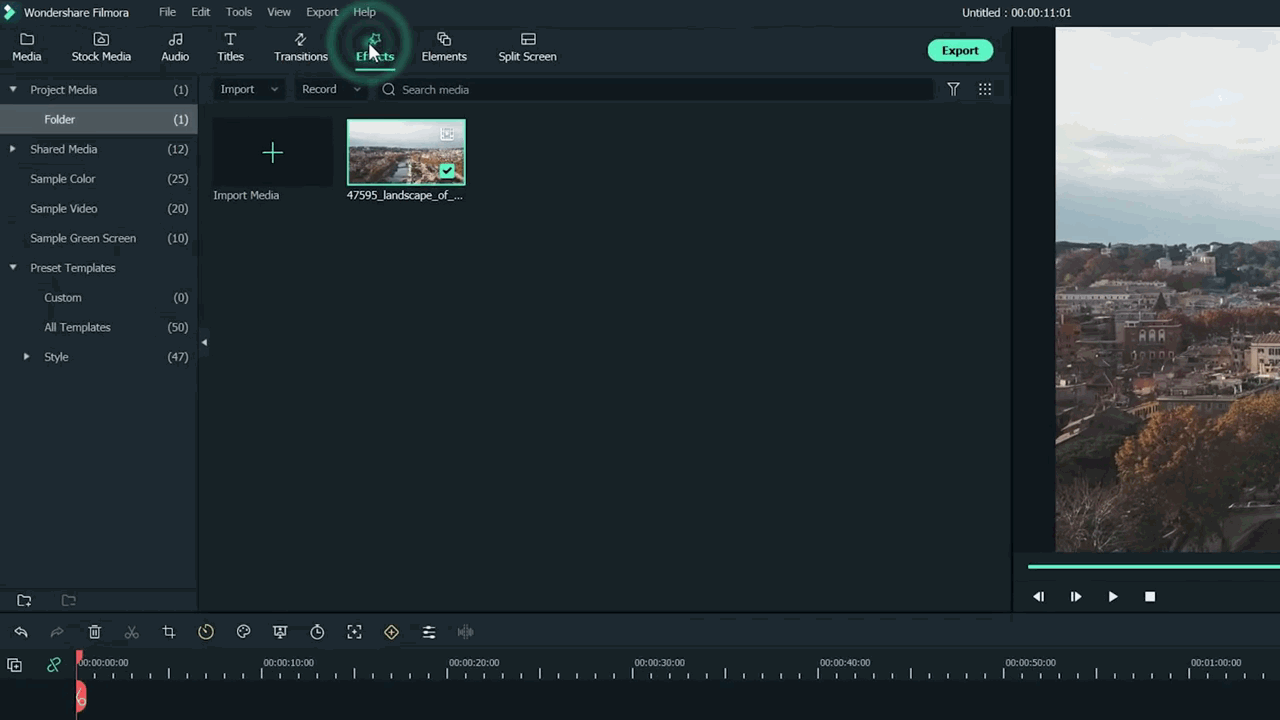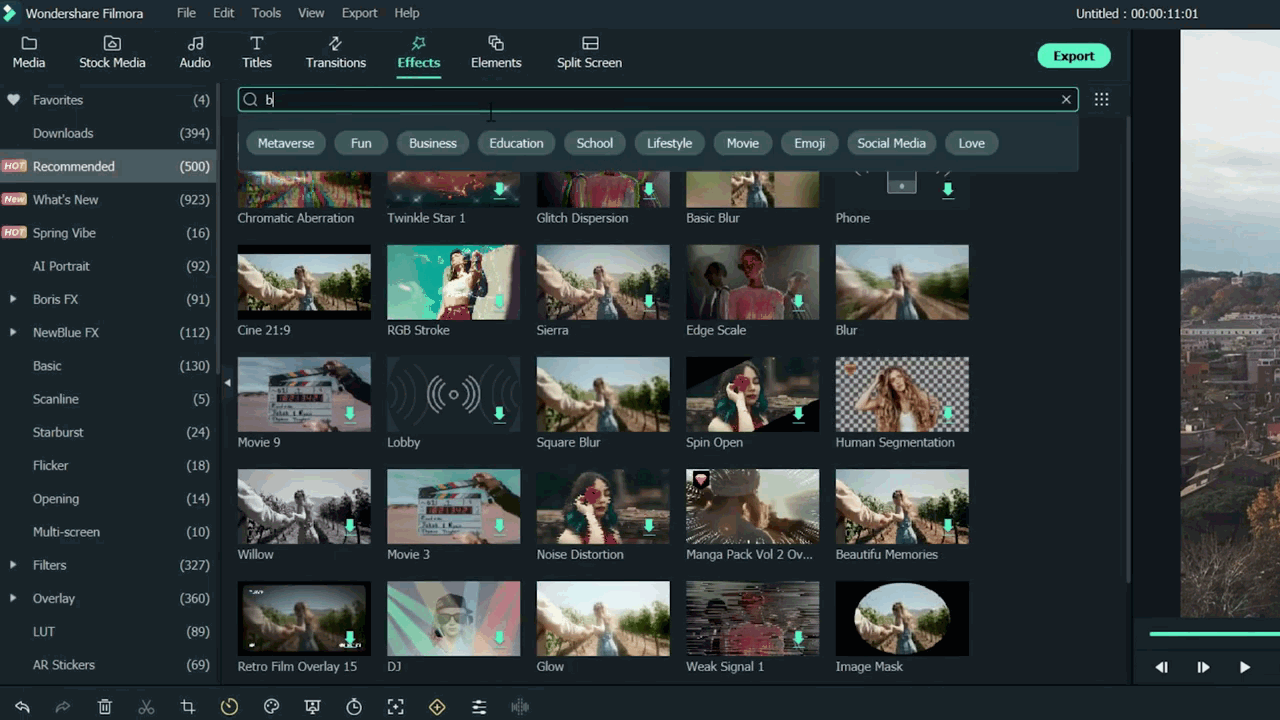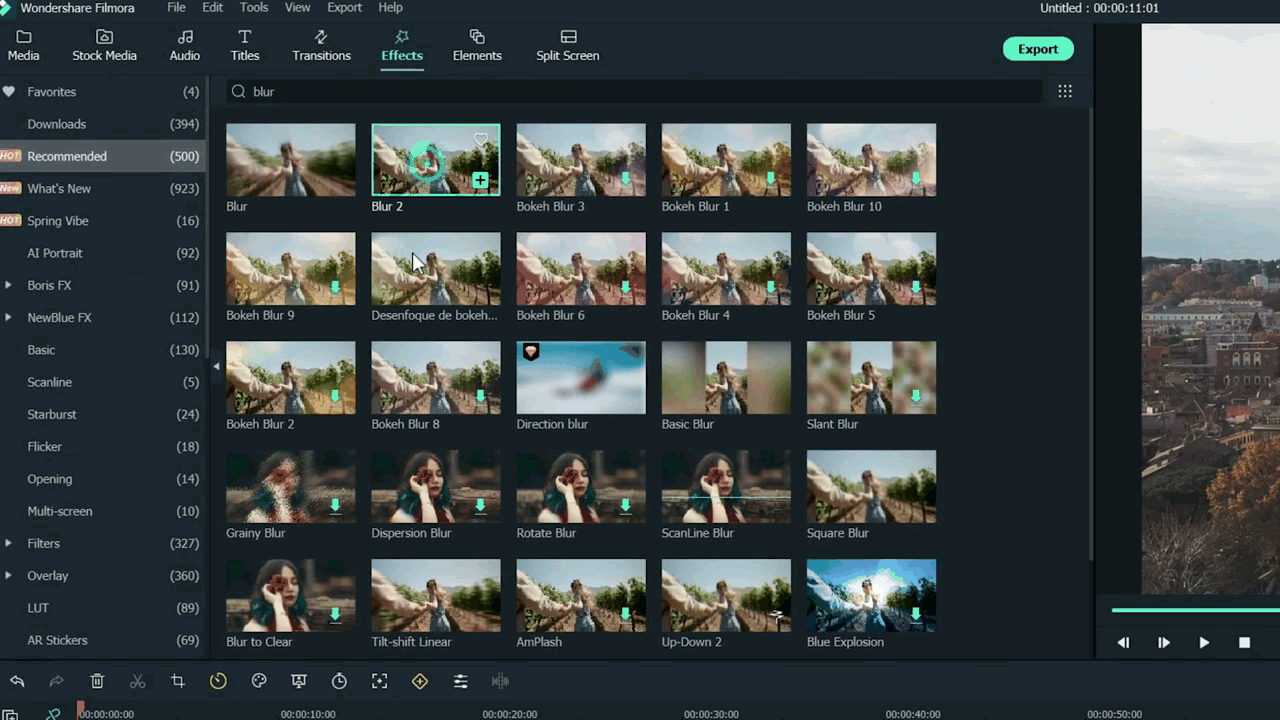
To add a blur effect from the panel, follow the below-mentioned steps:
- First of all, move toward the above tabs.
- Then click on the 5th section, which is Effect
- After selecting the effect tab, a new window will pop up.
- In this section, we have 500+ different effects.
- Then, click on the search bar.
- Search for the Blur effect.
- After that, click on the Blur 2
- Then Download this effect if you haven’t done this already.
Step4 Add the blur effect to the video
After selecting and downloading the blur effect, it’s time to add it to the video. Again, see how precise it turned out. To add effect, follow below steps:
- First, drag and Drop the effect toward the timeline.
- Then, make sure to release the effect on the video to give it a lens blur appearance.
Step5 Add the effect multiple times
Want to get an ideal blur level? If you need more blur level in your video and make it more cinematic, then follow the below steps:
- First, ensure that the opacity of the blur effect is 100%.
- Then, if you still want more blurriness, add Blur 2 effect multiple times on the video.
- Finally, add effect by just the Drag and Drop

Step6 Drop the same video clip
- Add the same video clip 2nd time on the timeline.
- Add it by just the Drag and Drop
- Make sure you add it to 2nd video track in the timeline above the first one.
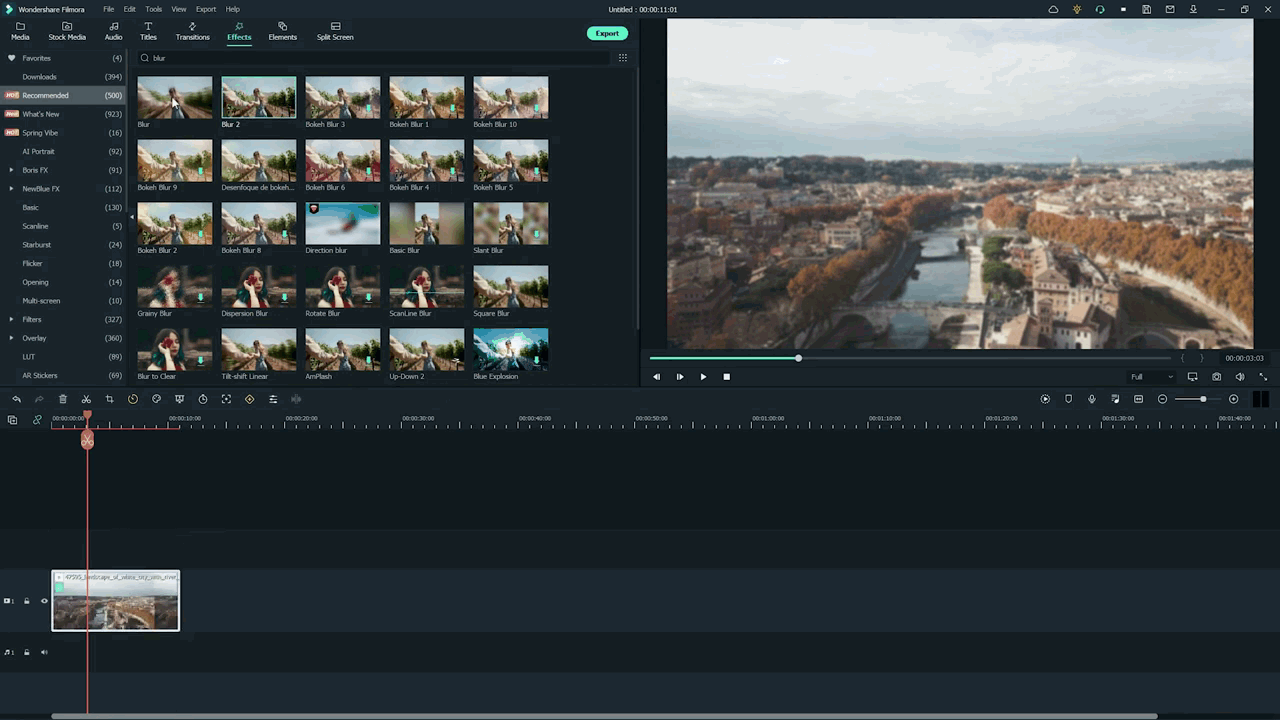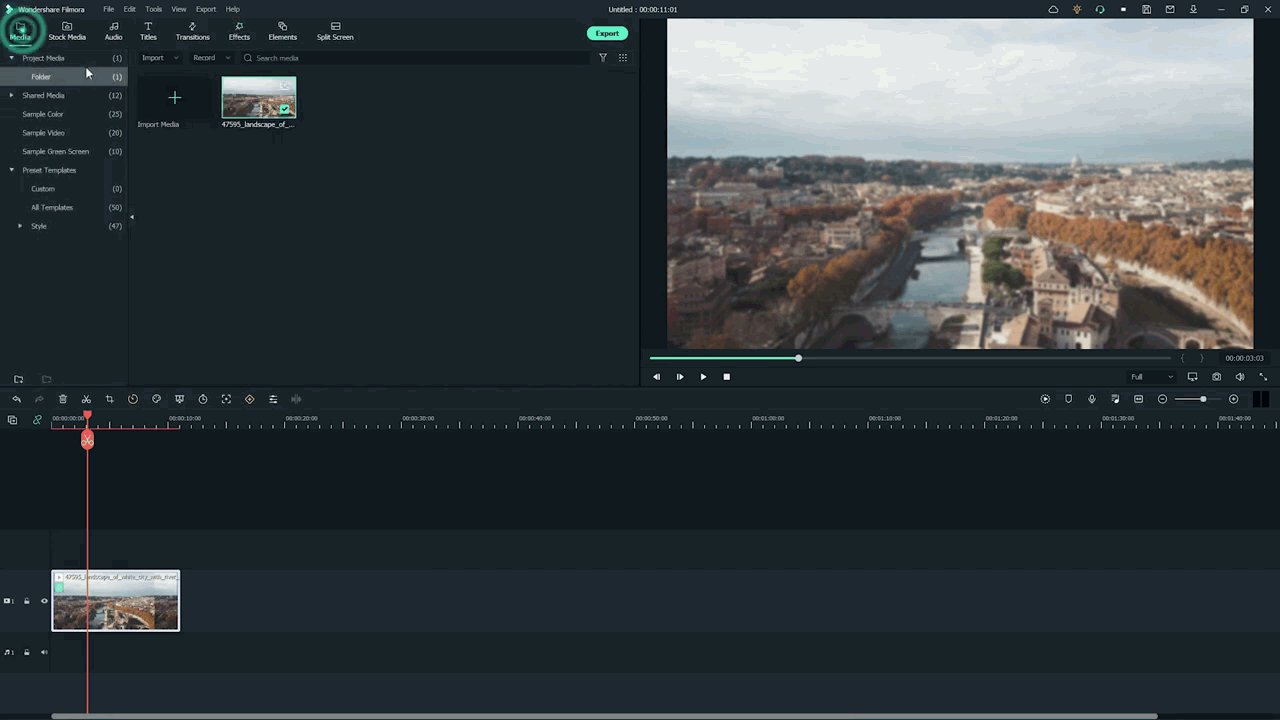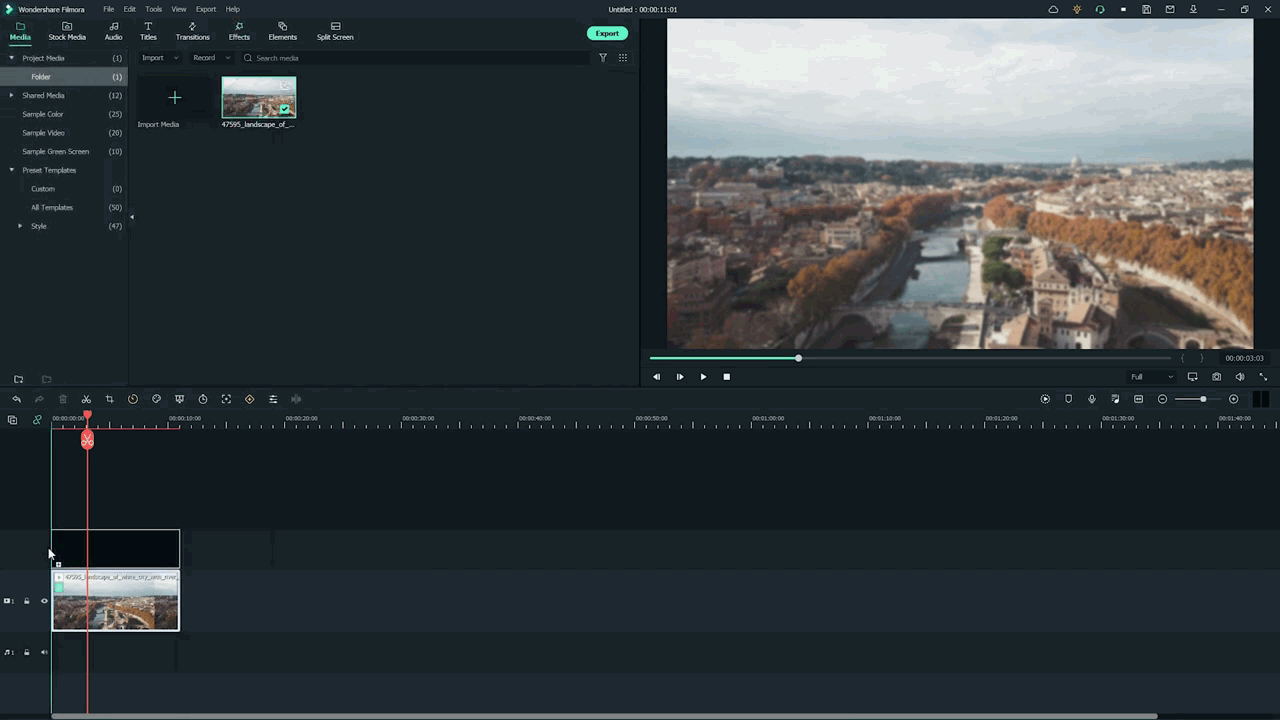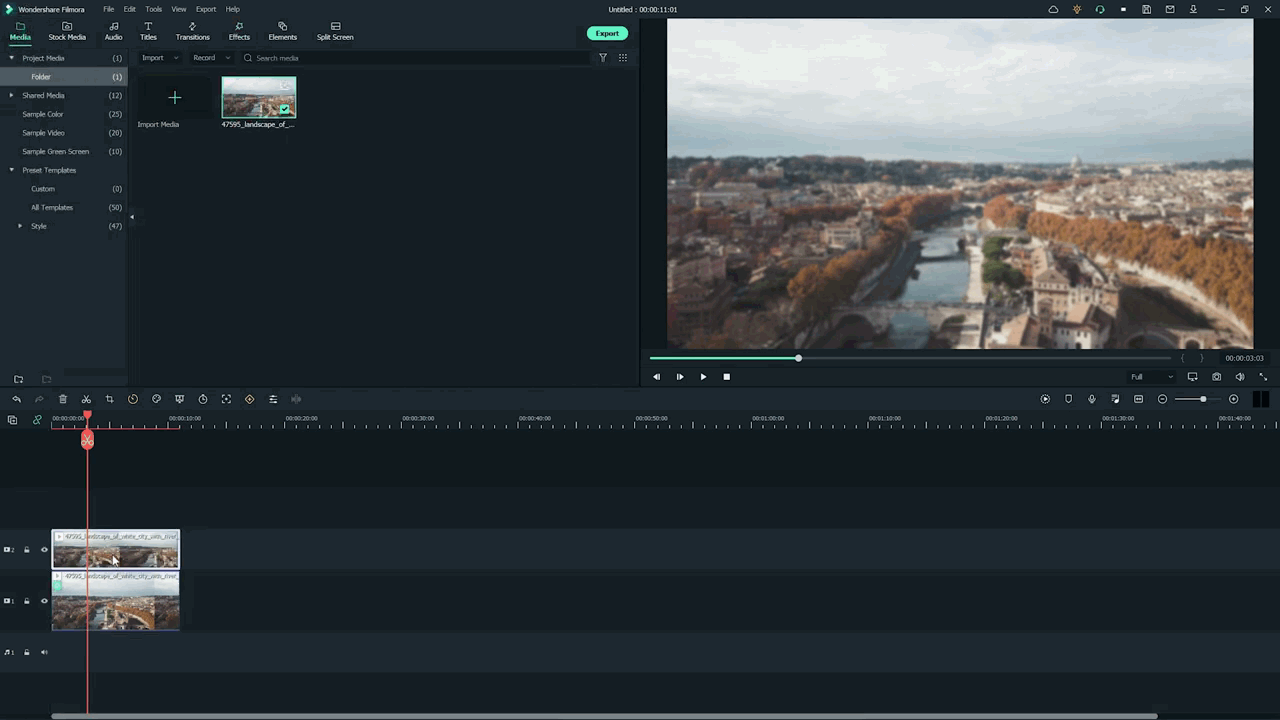
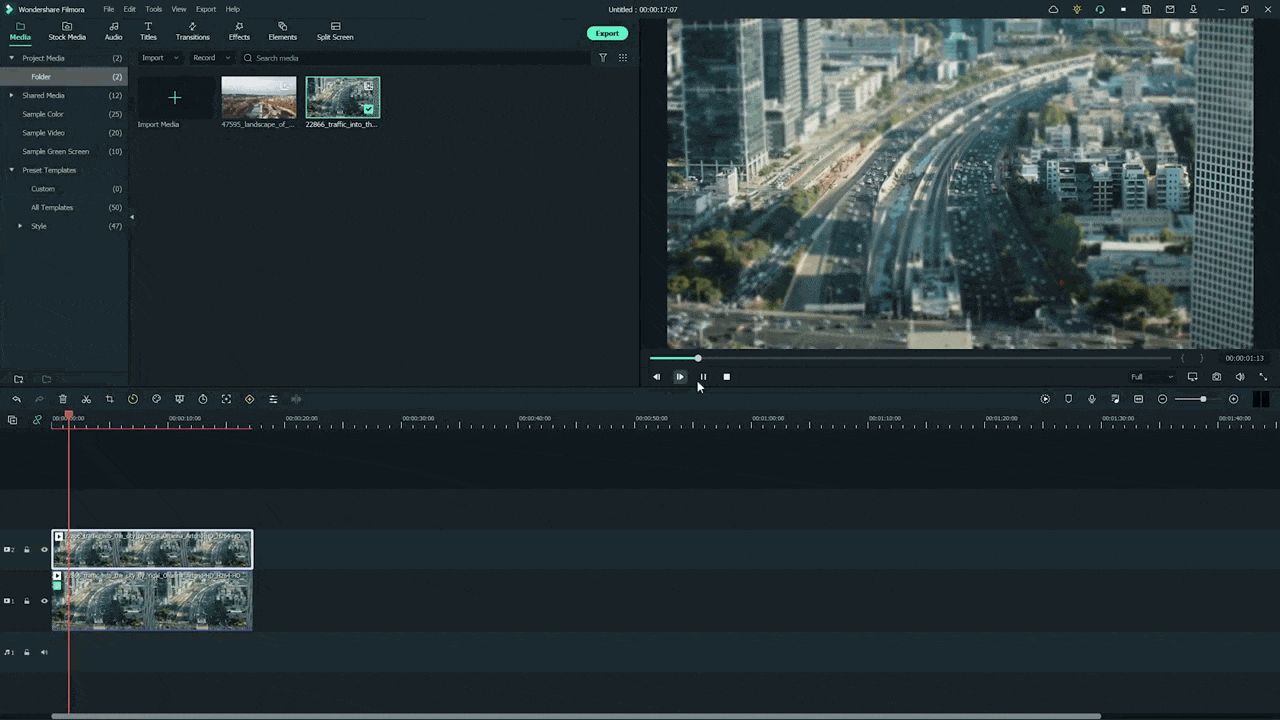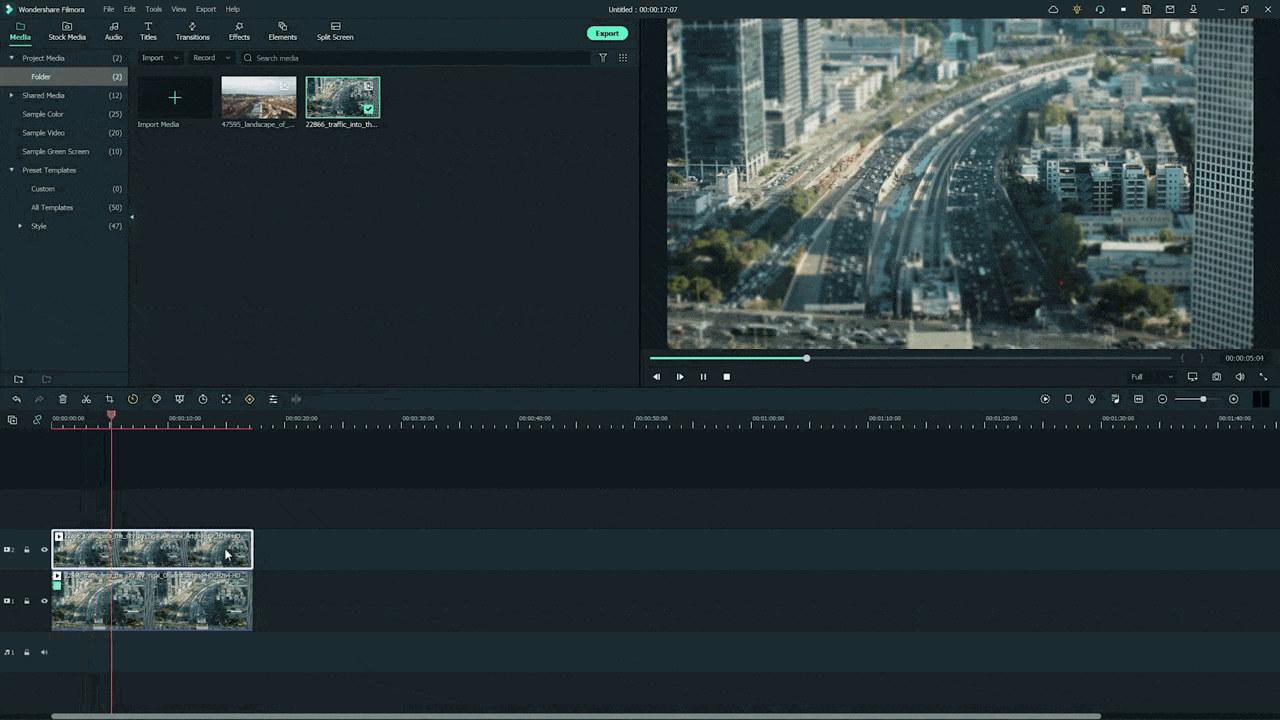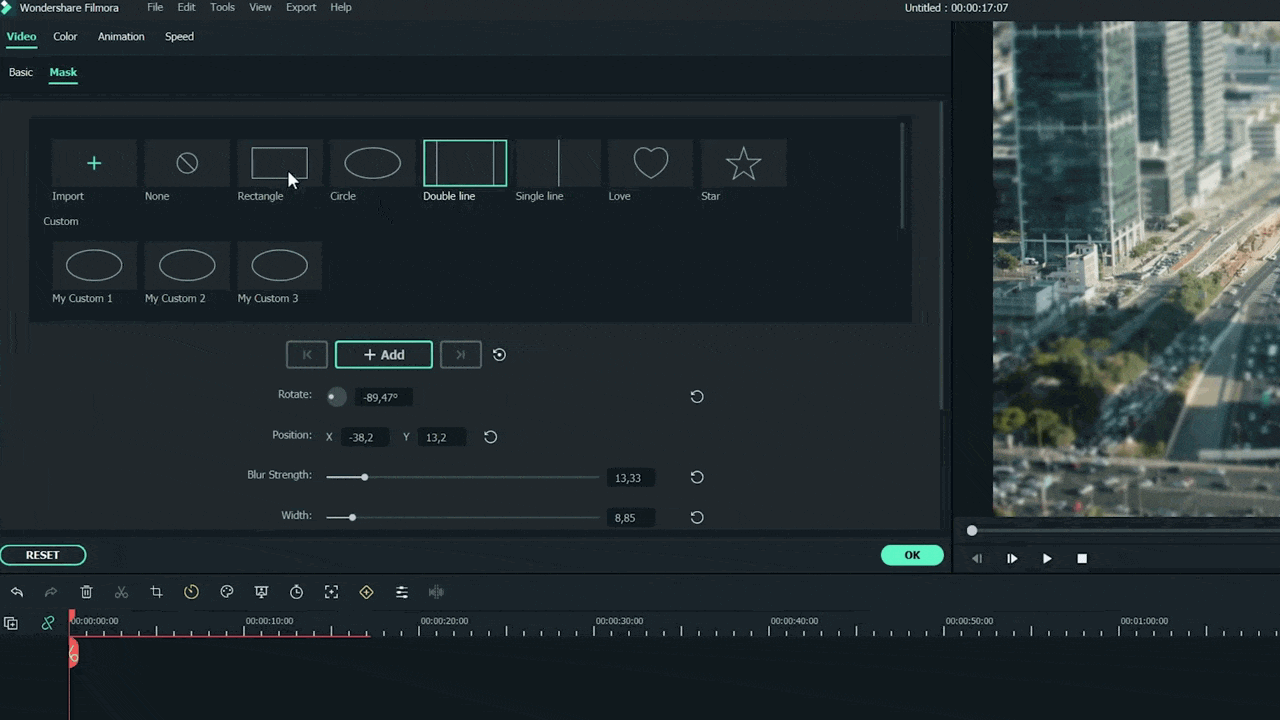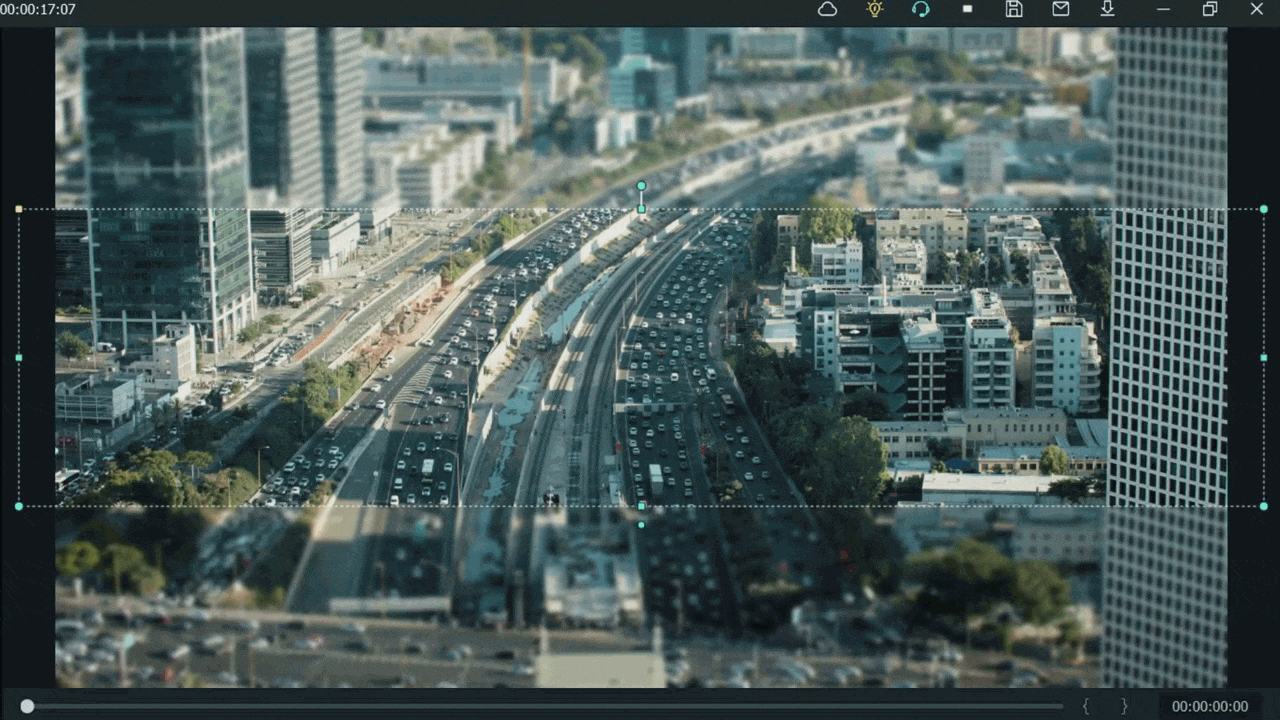
Step7 Add masks on the Video
Now, it’s time to select a specific video portion and add a mask. Due to this, we will have a selective blur portion. For this, follow the below guidelines:
- Double-click on the video present in 2nd track.
- The settings tab will be open in the top left section.
- Then find the Mask section and click on it.
- After this, click on the Double-line.
- Set the mask on video according to your style and choice.
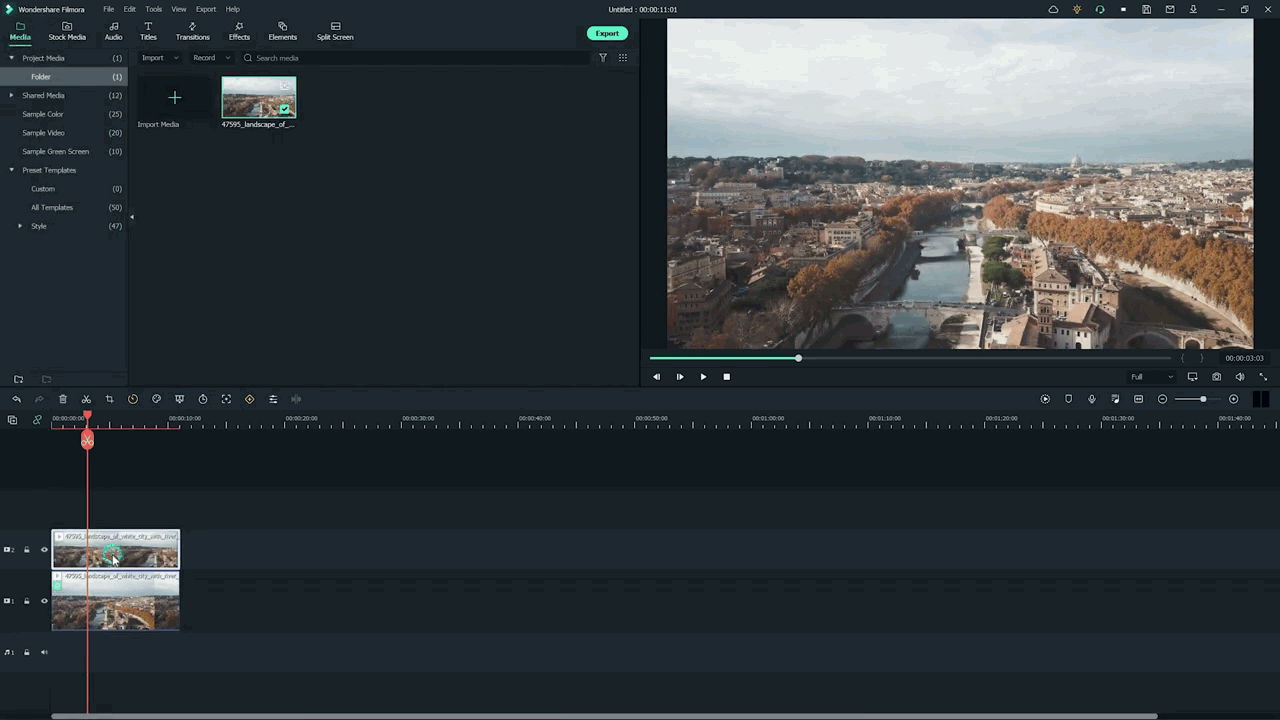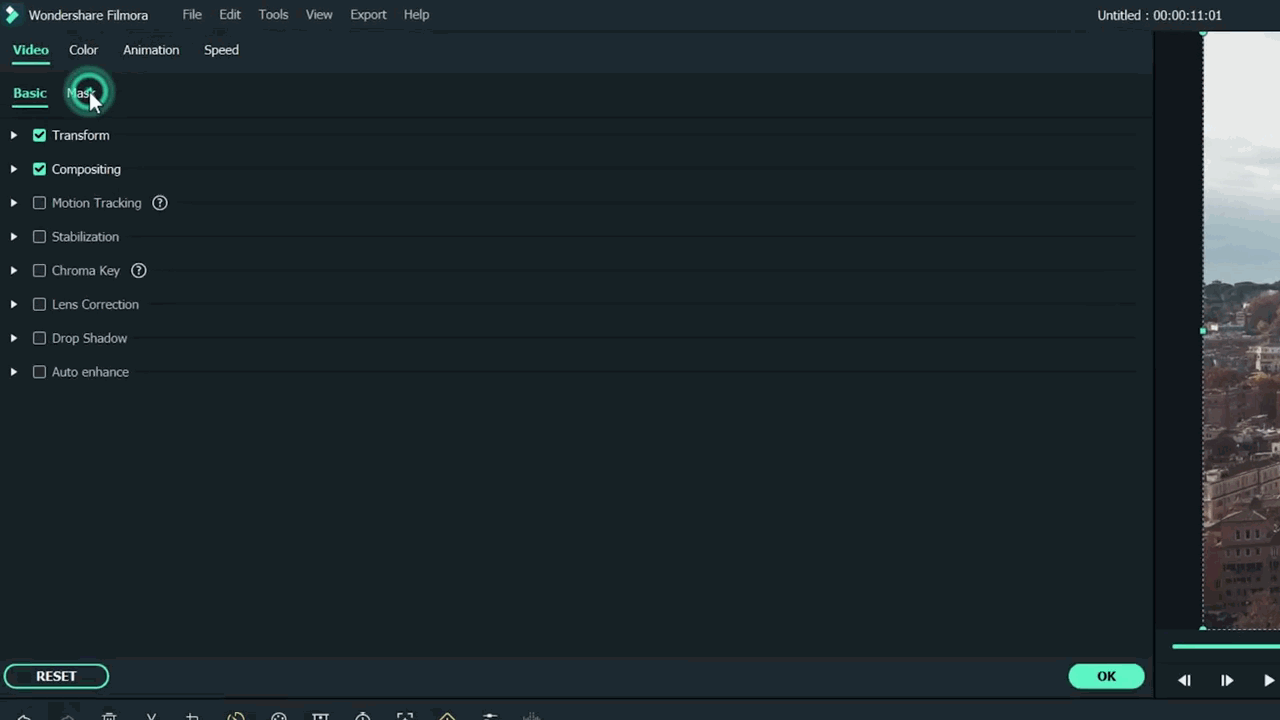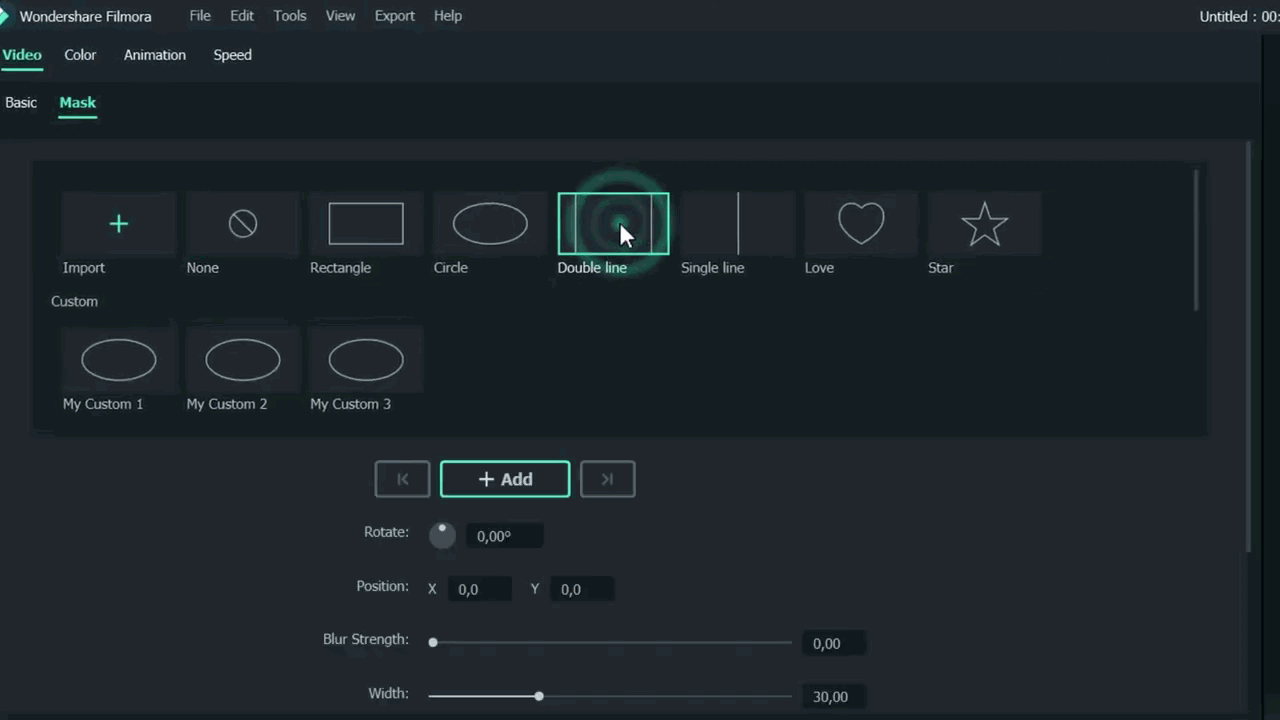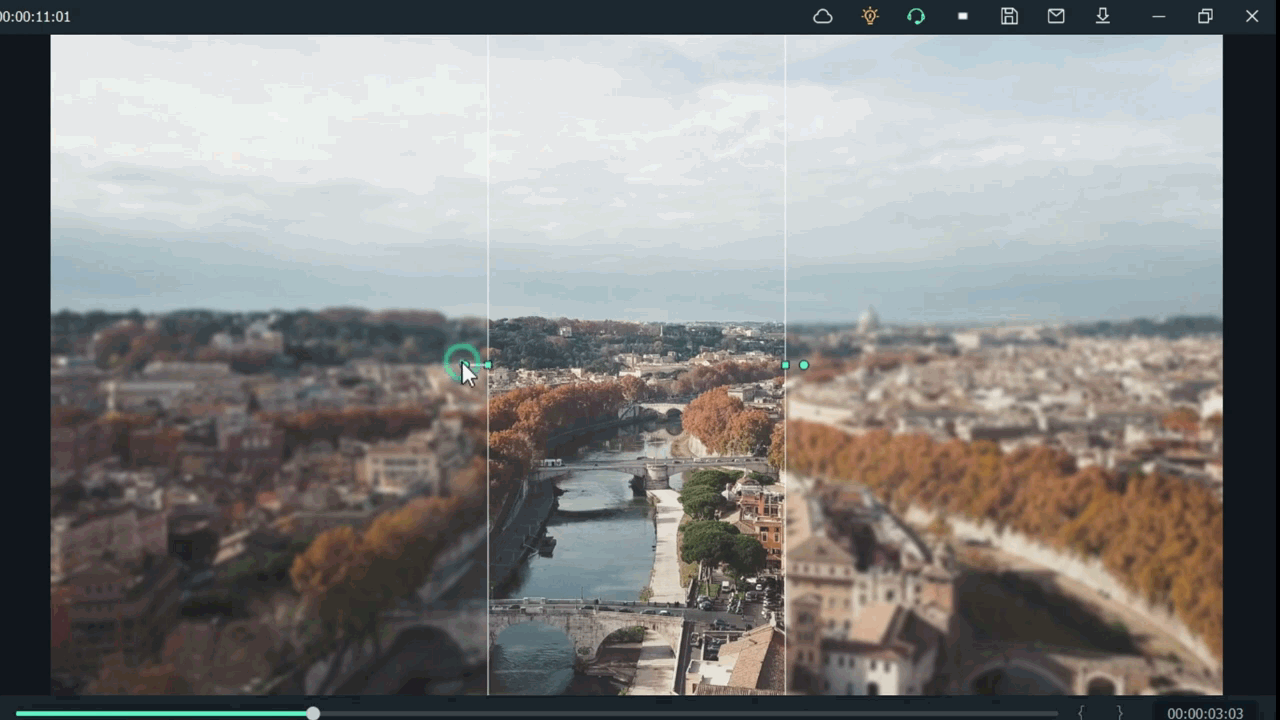
![]()
Note: you can adjust the mask size and position by rotating and changing its shape.
Watch the rotating and adjusting actions as shown below!
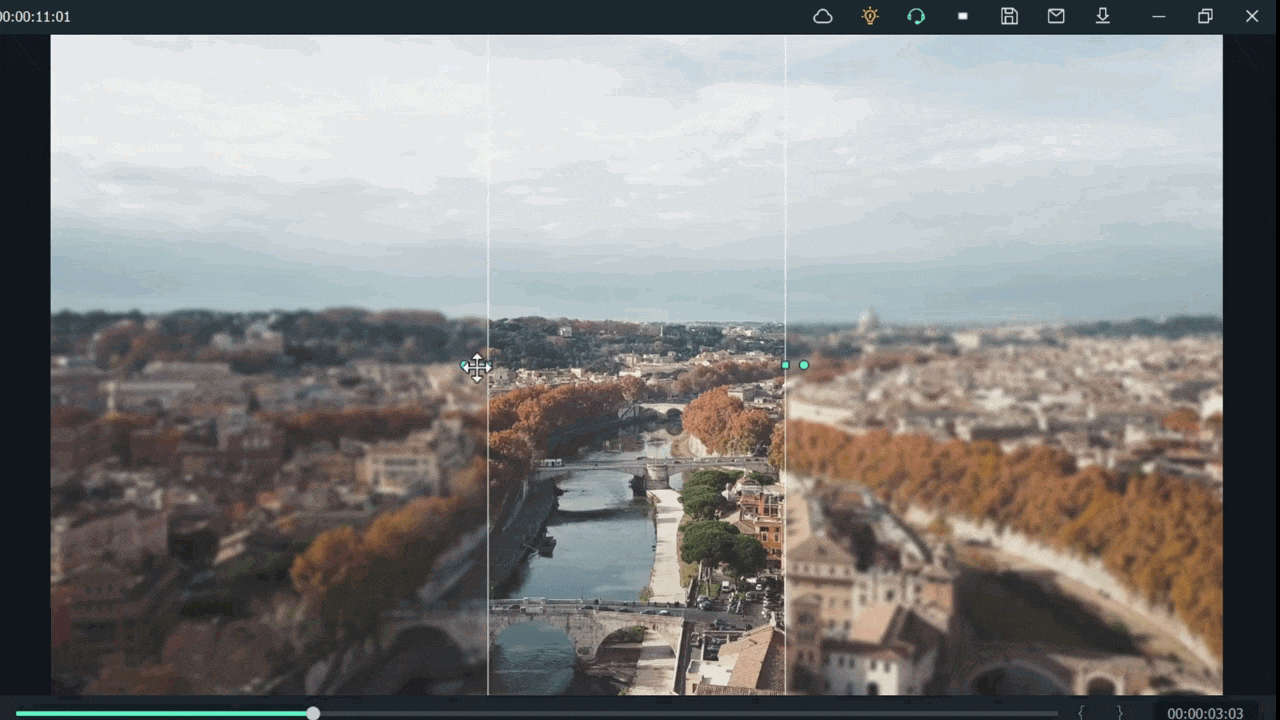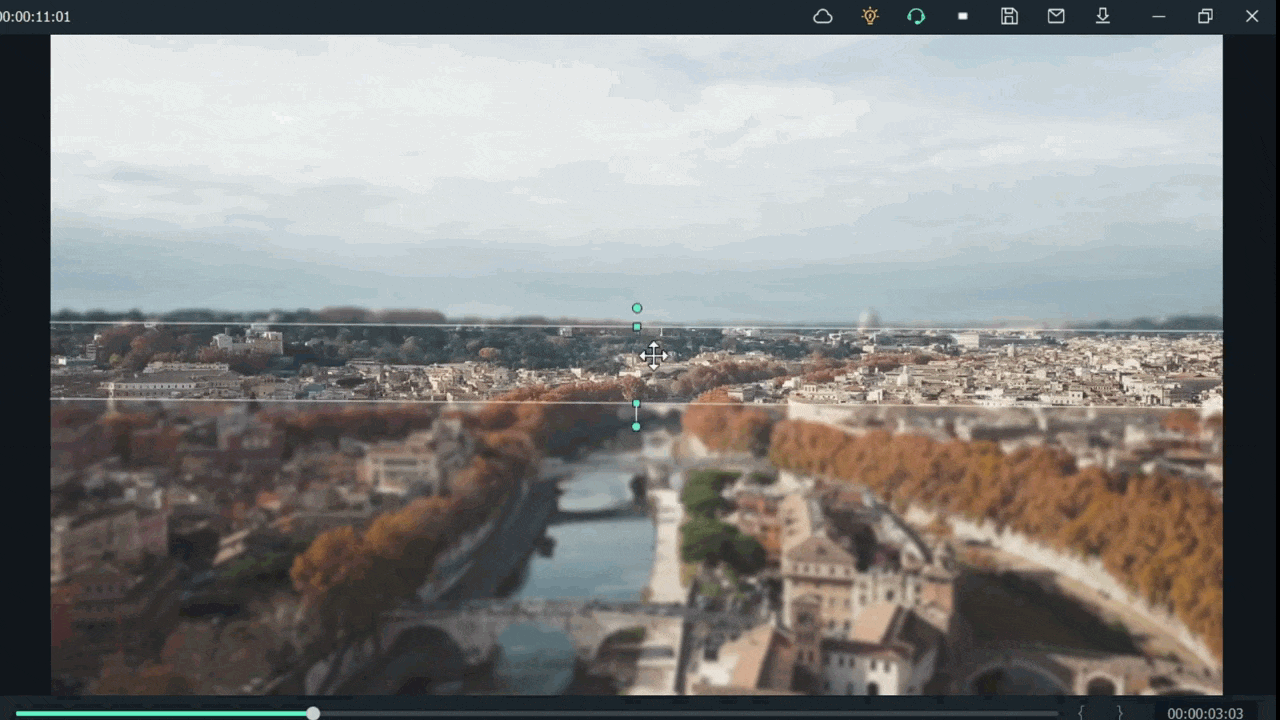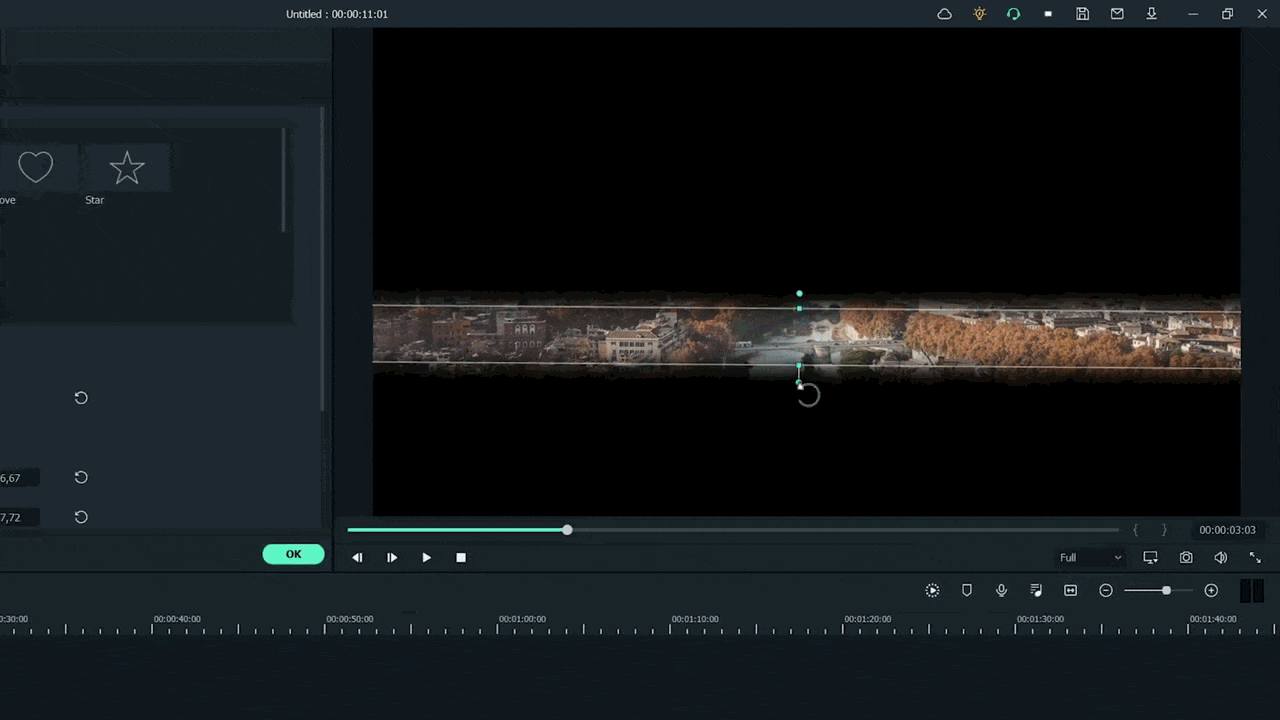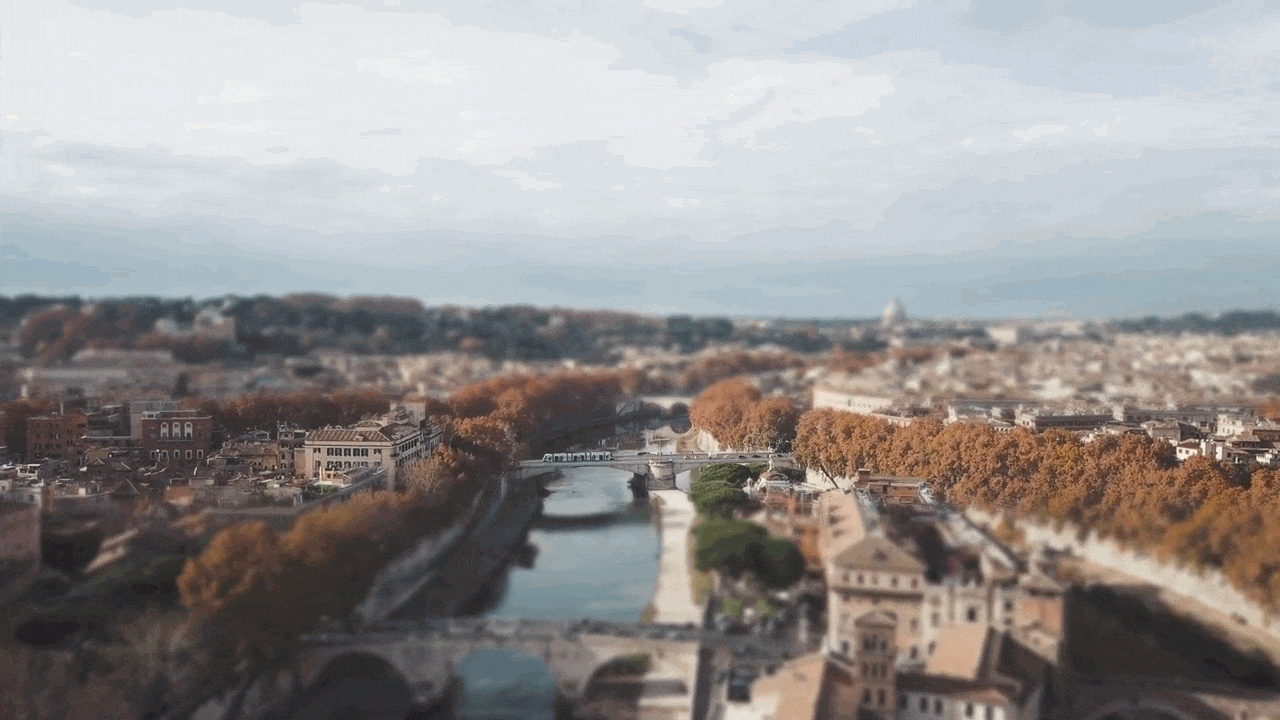
For example, when we add a mask in the below time-lapse video, follow the above mask adjustments. Unfortunately, we can’t get good results. Therefore, we will apply another way to add a mask by changing shape and position. Follow the instructions for modifications:
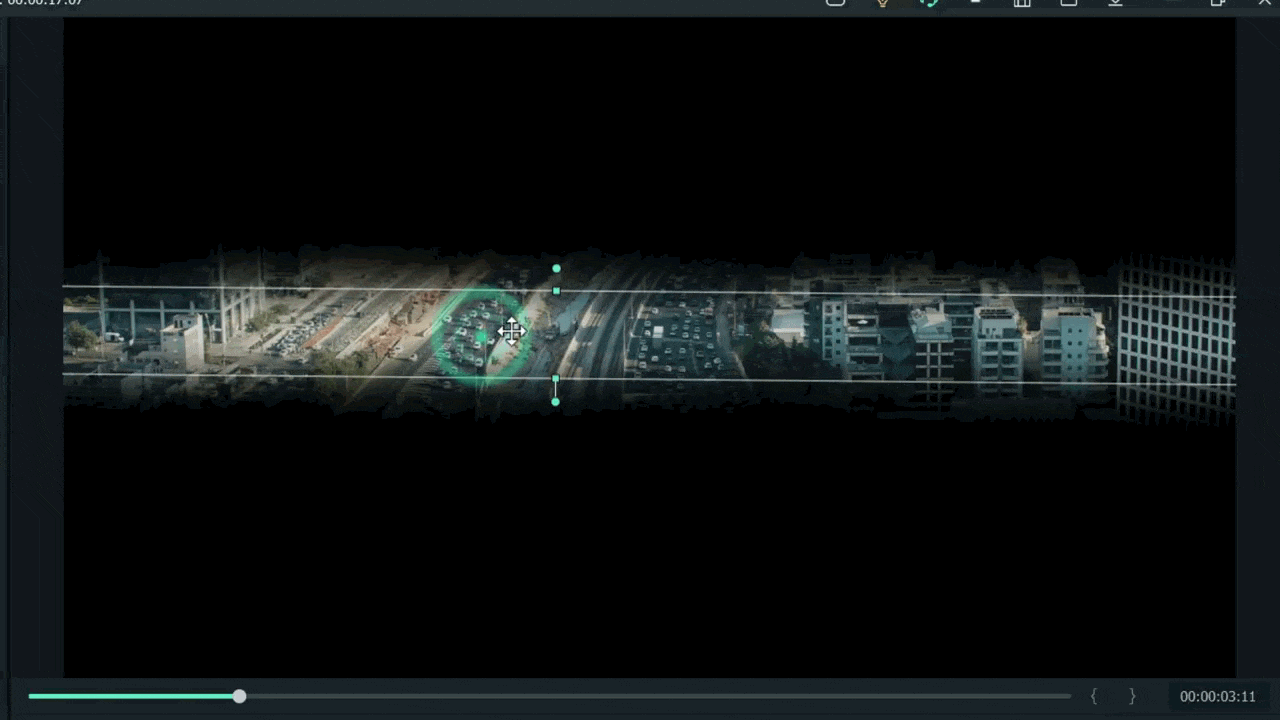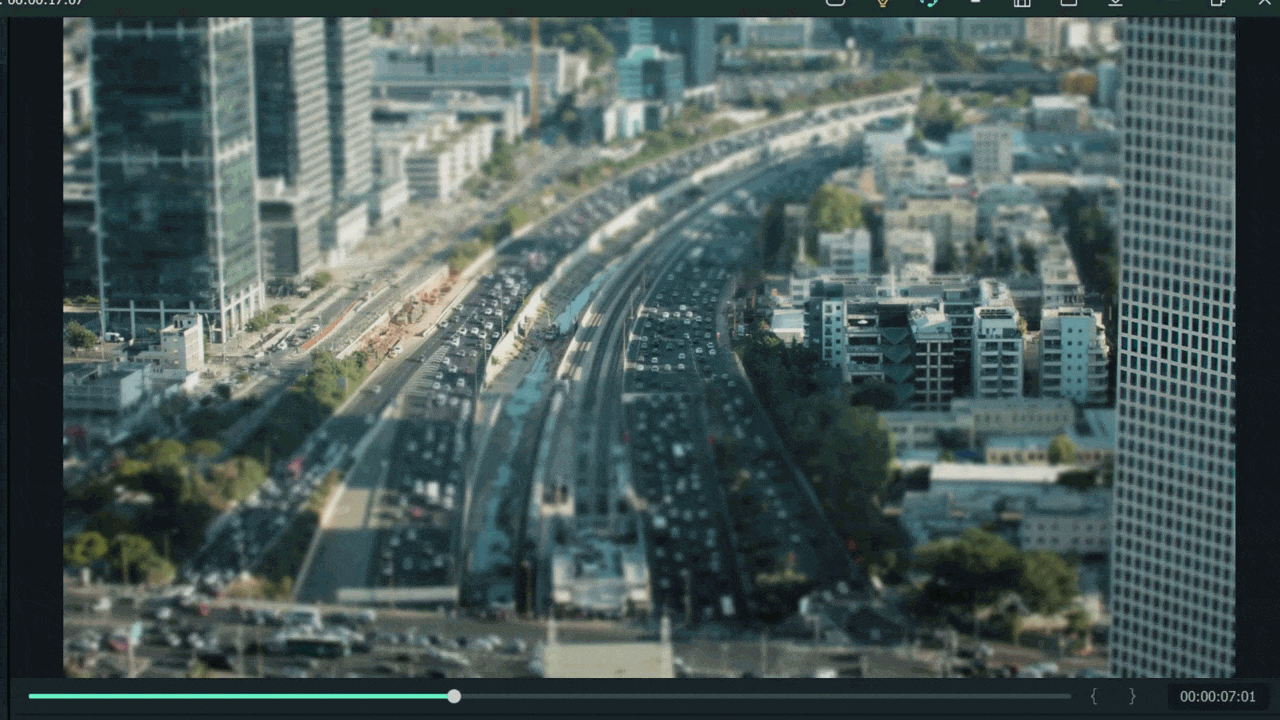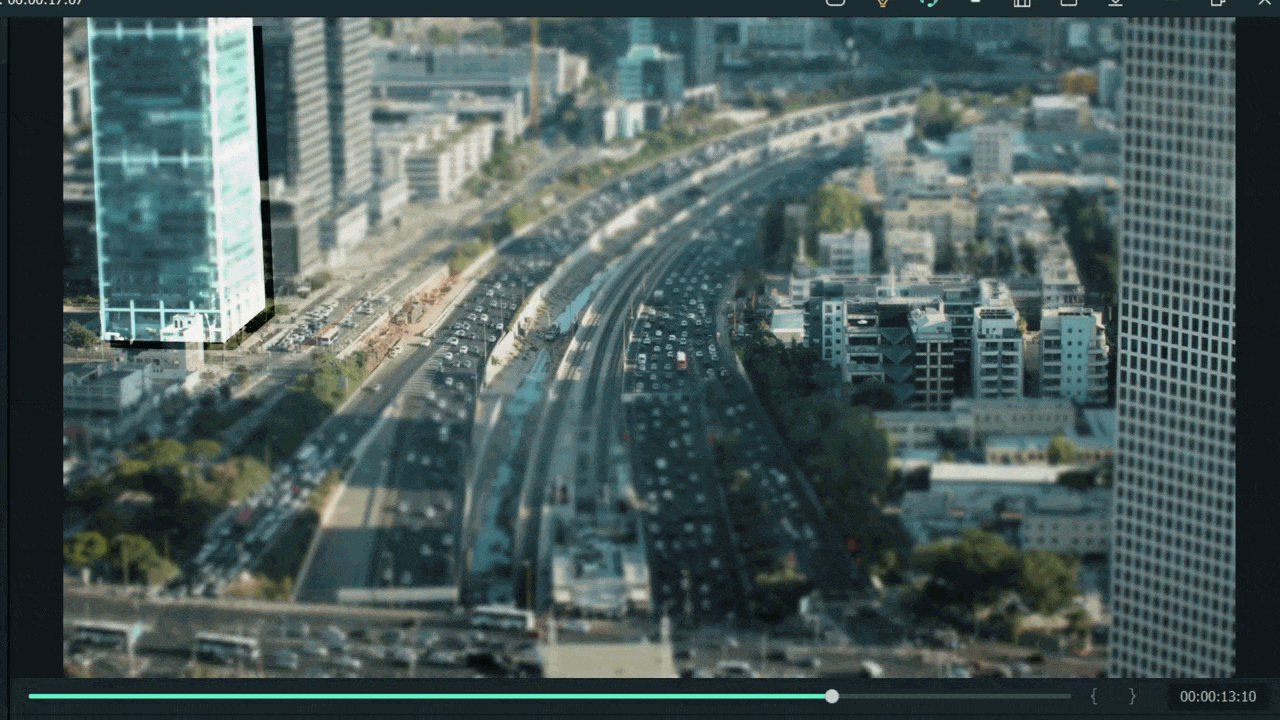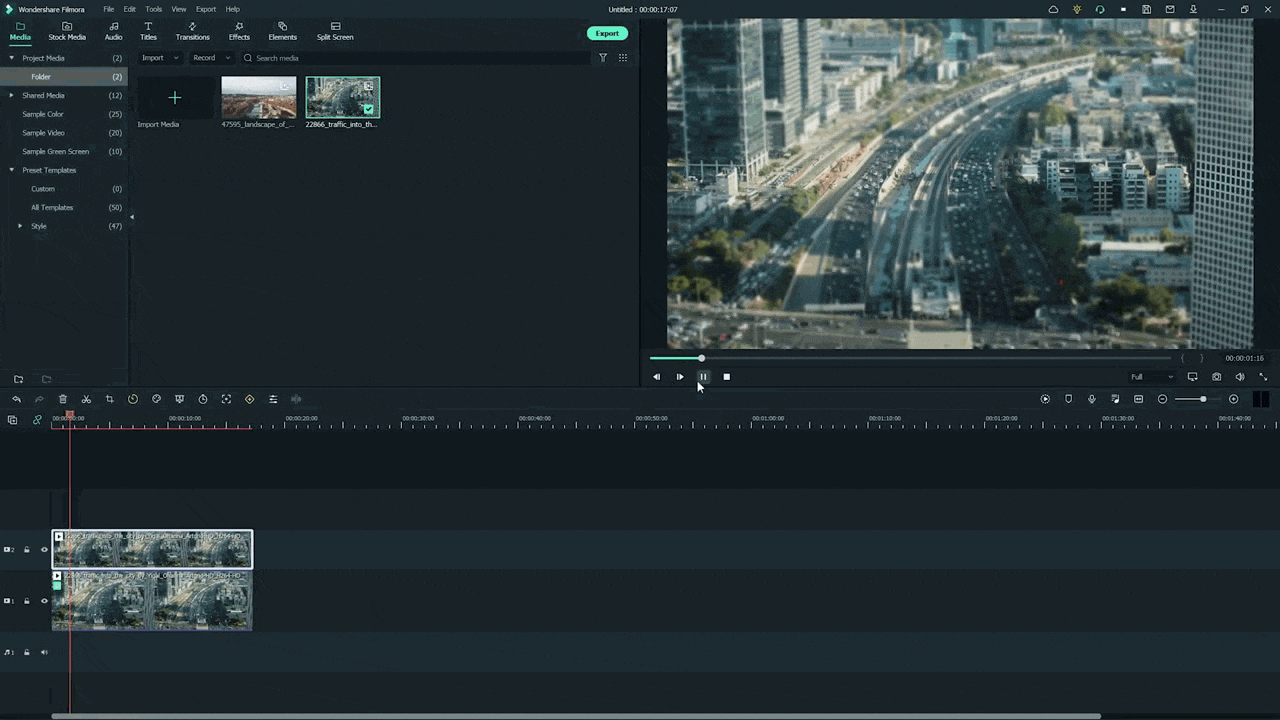
- Make a building or any object Blurry near the camera because it is not present within the depth of field.
- While the object is far from the camera, it is focused because it is in the depth of the field.
- Then adjust the mask, as per your choice.
Want to change the shape of the mask? Then follow the below steps:
- Double-click on the video present in 2nd video track.
- Settings will activate on the top left side.
- Then click on the Mask tab to open it.
- Select the Rectangular mask from the list and apply it.
![]()
Note: make sure you are masking the same extent and excluding the object you want to be out of focus.
Now, it’s time to mask the whole object, which is far, but we want to make it in focus! For this, follow these steps:
- Add the same stock video clip a third time on the third video track of the timeline.
- Then add a mask in a Rectangle shape on the building.
- Don’t blur the edge of this mask.
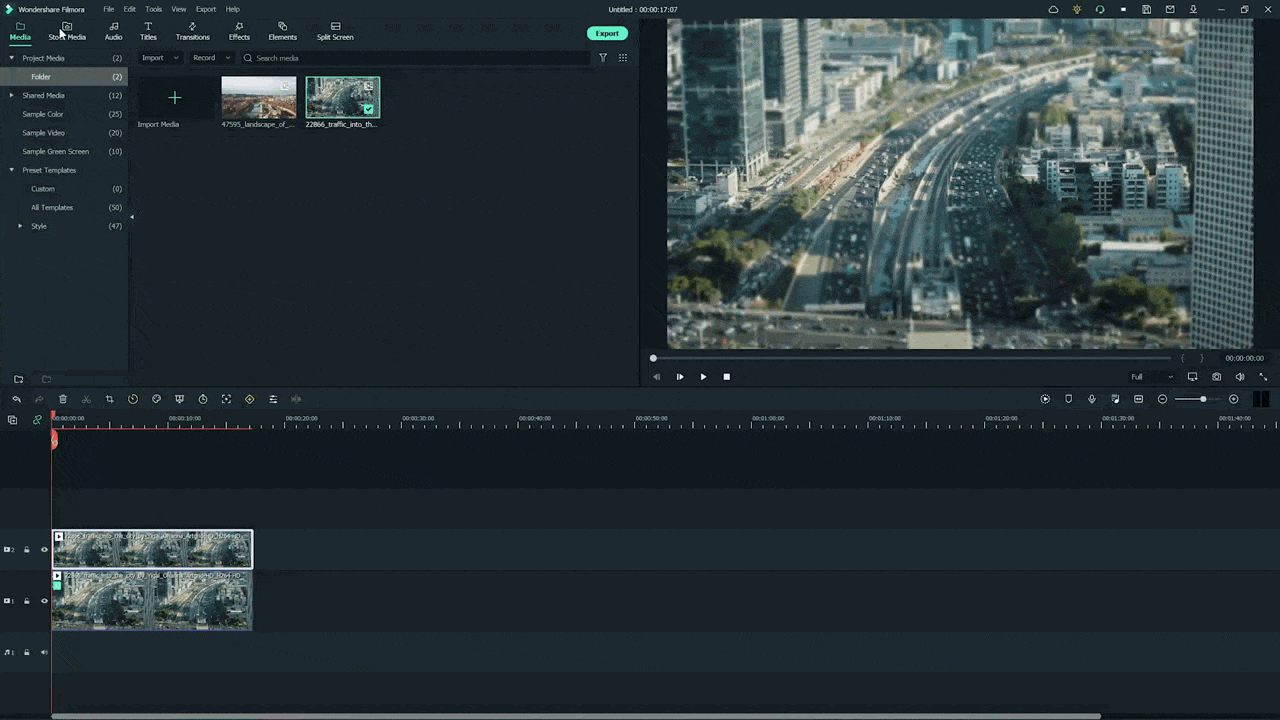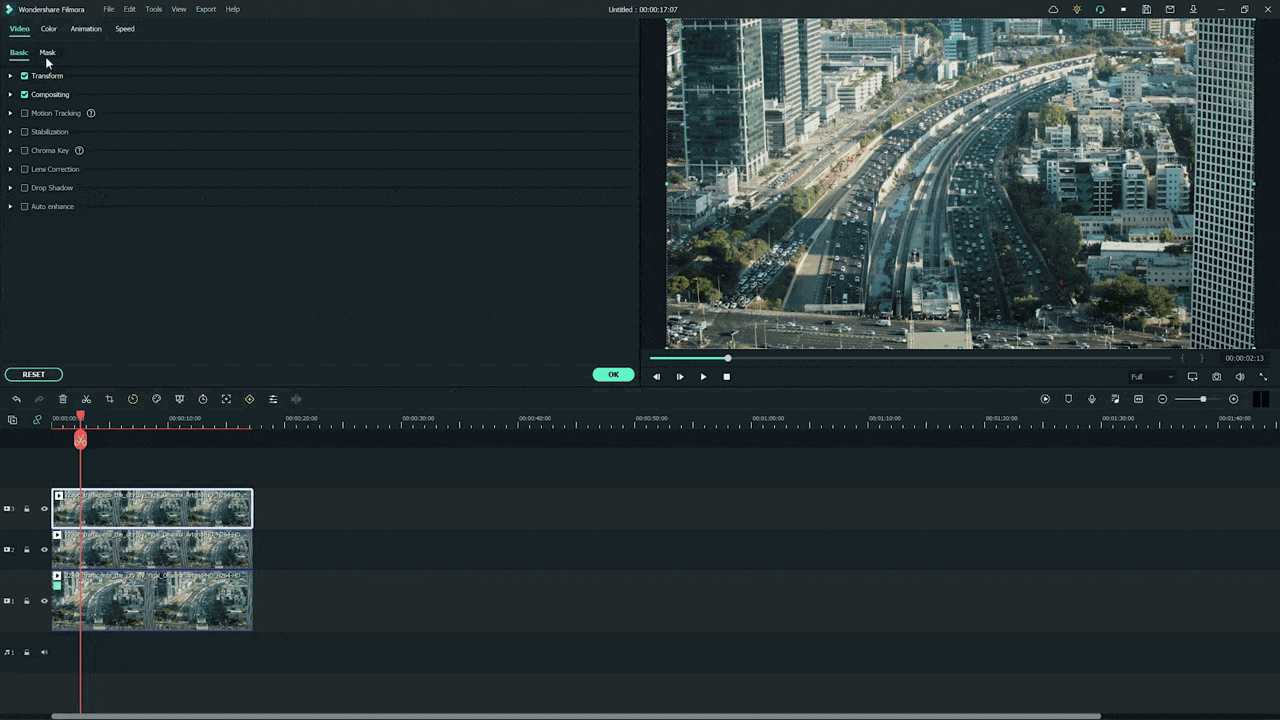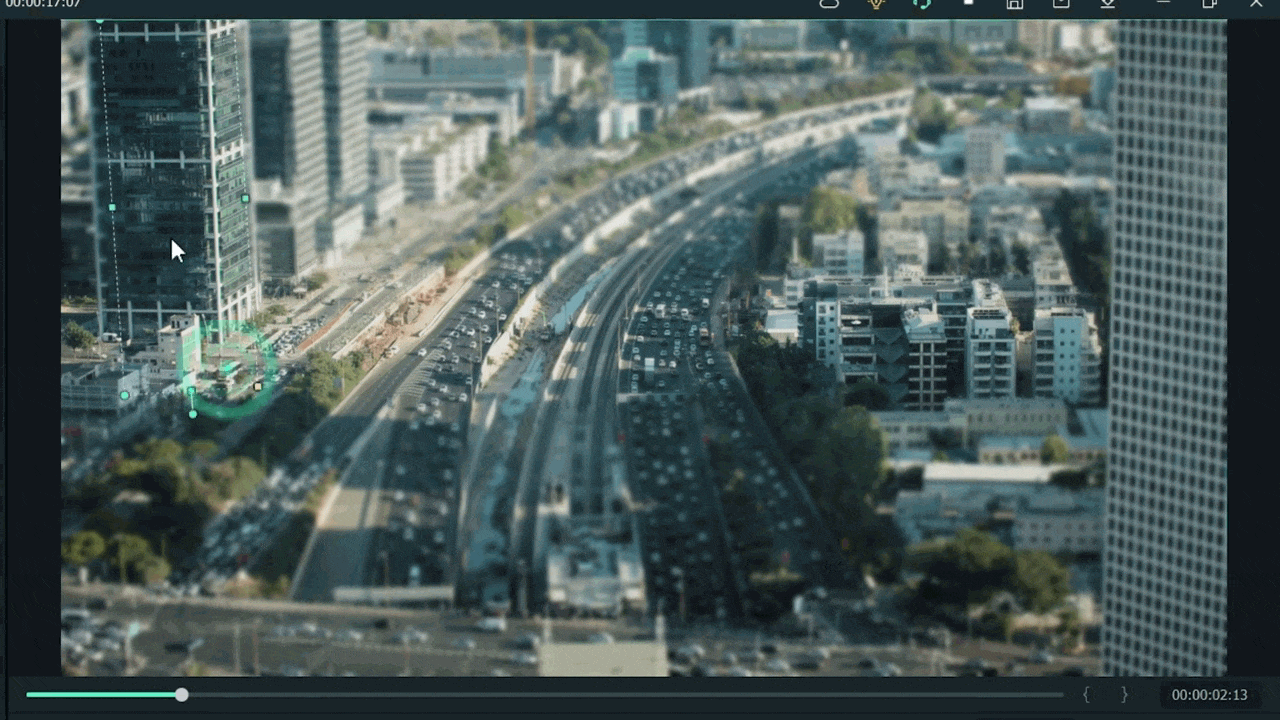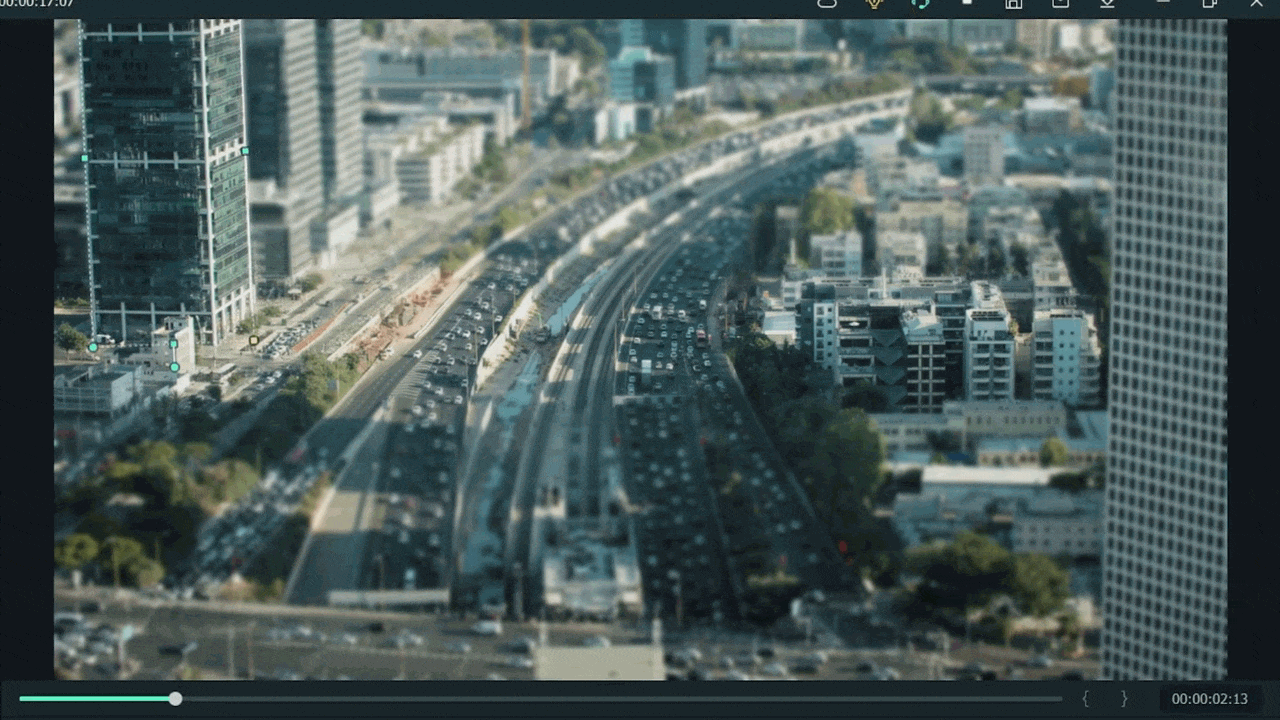
Step8 Final Look
You are excited now to see the final look of your miniature effect! Finally, it’s in front of you! Just modify it more if you want to make it more precise.

Have you tried to add a miniature effect before? If yes, then share your experience with us! Try with more mask shapes and add more blur effects. Make sure that you are using Wondershare Filmora to make more filmy shots. Feel free to try out different effects and enjoy the following results!
Free Download For Win 7 or later(64-bit)
Free Download For macOS 10.14 or later
Step2 Choose any stock footage
If you don’t have good-quality footage, but want to boost your video, here is how. You can get the miniature effect without a big format view camera or specialized lens.
- Open Filmora and select any stock footage in Wondershare Filmora.

Move to the stock media folder on the above bar in the Wondershare Filmora. Or you can look towards the left window, where you will see the sample videos tab.
- Click on the sample videos tab, and a new window will appear on the library screen.
Here you will see almost more than 20 videos. So, instead of using the actual recorded footage, we’ll make do with what we have by default. After selecting and adding the stock footage of your choice. Then you have to follow the below process:
- First, hold the Stock Footage as shown in the folder section.
- Then Drag and Drop it to the timeline section for further editing.

Who will get Stock Media?
Want to get stock media? You can only have access to the stock media library if you already buy the license of Wondershare Filmora.
- The latest version has an unlimited stock library.
- After purchasing any plan, you can access Stock Media (Unsplash, Giphy, Pixabay, Pixel).
Step3 Head to the effect panel
As we are working on miniature effects, what do we need first? First, we ensure that we have a Blur effect on the video.

To add a blur effect from the panel, follow the below-mentioned steps:
- First of all, move toward the above tabs.
- Then click on the 5th section, which is Effect
- After selecting the effect tab, a new window will pop up.
- In this section, we have 500+ different effects.
- Then, click on the search bar.
- Search for the Blur effect.
- After that, click on the Blur 2
- Then Download this effect if you haven’t done this already.
Step4 Add the blur effect to the video
After selecting and downloading the blur effect, it’s time to add it to the video. Again, see how precise it turned out. To add effect, follow below steps:
- First, drag and Drop the effect toward the timeline.
- Then, make sure to release the effect on the video to give it a lens blur appearance.

Step5 Add the effect multiple times
Want to get an ideal blur level? If you need more blur level in your video and make it more cinematic, then follow the below steps:
- First, ensure that the opacity of the blur effect is 100%.
- Then, if you still want more blurriness, add Blur 2 effect multiple times on the video.
- Finally, add effect by just the Drag and Drop

Step6 Drop the same video clip
- Add the same video clip 2nd time on the timeline.
- Add it by just the Drag and Drop
- Make sure you add it to 2nd video track in the timeline above the first one.

Step7 Add masks on the Video
Now, it’s time to select a specific video portion and add a mask. Due to this, we will have a selective blur portion. For this, follow the below guidelines:
- Double-click on the video present in 2nd track.
- The settings tab will be open in the top left section.
- Then find the Mask section and click on it.
- After this, click on the Double-line.
- Set the mask on video according to your style and choice.

![]()
Note: you can adjust the mask size and position by rotating and changing its shape.
Watch the rotating and adjusting actions as shown below!

For example, when we add a mask in the below time-lapse video, follow the above mask adjustments. Unfortunately, we can’t get good results. Therefore, we will apply another way to add a mask by changing shape and position. Follow the instructions for modifications:

- Make a building or any object Blurry near the camera because it is not present within the depth of field.
- While the object is far from the camera, it is focused because it is in the depth of the field.
- Then adjust the mask, as per your choice.
Want to change the shape of the mask? Then follow the below steps:

- Double-click on the video present in 2nd video track.
- Settings will activate on the top left side.
- Then click on the Mask tab to open it.
- Select the Rectangular mask from the list and apply it.
![]()
Note: make sure you are masking the same extent and excluding the object you want to be out of focus.
Now, it’s time to mask the whole object, which is far, but we want to make it in focus! For this, follow these steps:
- Add the same stock video clip a third time on the third video track of the timeline.
- Then add a mask in a Rectangle shape on the building.
- Don’t blur the edge of this mask.

Step8 Final Look
You are excited now to see the final look of your miniature effect! Finally, it’s in front of you! Just modify it more if you want to make it more precise.

Have you tried to add a miniature effect before? If yes, then share your experience with us! Try with more mask shapes and add more blur effects. Make sure that you are using Wondershare Filmora to make more filmy shots. Feel free to try out different effects and enjoy the following results!
Free Download For Win 7 or later(64-bit)
Free Download For macOS 10.14 or later
How do you set up DaVinci scopes? The internal color scopes in Resolve are flexible and customizable but can be confusing. The built-in DaVinci Resolve scope used to be limited only a few possibilities. However, the new 9-scope view offers a wider range of choice, making them a powerful tool for video editing. In this article, we will explore how to set up DaVinci scopes to achieve better color results.
Color Correction Editor An easy-to-use video editor helps you make color correction and color grading experience for videos!
Free Download Use Vectorscope in Filmora Try Color Correction

Part 1. Unlocking Color Precision: Exploring the Improved Scopes in DaVinci Resolve
The Blackmagic Design continues to improve the Resolve to make it better with every iteration. The new features improve colorist workflow in less powerful ways. The major improvements include a major facelift to the scope, allowing professions to do more with DaVinci resolve. Let’s have a look at some of these changes:
1. CIE 1931 Color Space
The inclusion of the CIE chromaticity diagram is perhaps the biggest change to DaVinci scopes. It displays the gamut of the project as set in the Color Management preferences. This makes it a useful alternate way of looking at the trace of an image to judge when the values are out of legal range. It also functions as an educational tool for learning about the range of color spaces.
2. Low Pass Filter
The wavefront and parade scopes now have a low pass filter, which reduces noise in the trace. This visually sharpens the display of the scopes, allowing easier detection of elements in the frame.
The image above shows the major improvements. The second set of waveforms has more defined lines. These have the low-pass filter activated, which makes the scopes easier to read.
3. High, Mid, and Low Views in Vectorscope
The vectorscope has been added to the ability to toggle the mid-tones, shadows, and highlights of the image independently. You can set the ranges with greater visualization control.
As seen in the picture above, the vectorscope controls allow you to select the low, mid, or high range of the image. You can also set the low and high ranges as desired.
4. Histograms Over Curves
Another great DaVinci scope is the histogram, which now appears outside of the scope panel. The new improvements have embedded the histogram inside the Curves tab on the bottom Palette. Click on the three dots in the Custom Curves tab. The pulldown menu that appears includes the Input or Output of the histogram. With these settings, you can find the element in the frame that helps you make adjustments quickly.
5. Scope Quality
The GPU-accelerated scopes engine allows the scopes to respond quickly. Users have the option to set the quality to high, medium, or low and the scopes will respond to a range of hardware systems. Depending on whether you are working on a stationary short or looking to see how the scopes react in real-time, you will be able to toggle the modes quickly and easily.

6. YRGB View in Histogram and Parade
The histogram and parade now come with the ability to view luminance together with the red, green, and blue channels. Users also have the option for YCbCr mode in the Parade.

7. Extents
These are weak elements in the signore, which are of lesser importance compared to the stronger elements. However, Danvici now allows them to be revealed for a full illustration of the information that lies in the image. Consequently, extents can be used to determine whether the data is being clipped beyond legal limits.

Part 2. Mastering Scopes in DaVinci Resolve: A Brief Guide
DaVinci scopes help you to analyze images as a basis for color correction. When used properly, scopes help in fixing white balance issues and checking saturation. They also allow you to get the correct exposure and check details like skin tone. To use scopes in DaVinci Resolve, go to the color page in the bottom right corner. You can also click on the small graph icon to view the scope. Here is how to use them:
1. Waveform
The Waveform represents the brightness or luminance of your image. In this video scope, the brightest parts are at the top while the darkest are at the bottom. The pixels are represented from left to right.
The Waveform scope on DaVinci Resolve is helpful when you are checking for clipping. This simply means finding out whether the image is too bright or too dark. The waveform also ensures that the image is properly exposed. The colorize feature of the waveform shows the colors of the image while the extent shows the darkest or lightest parts of the image.
2. Parade (RGB)
The RGB Parade comprises 3 waveforms that represent the luminance of red, green, and blue channels. The approach for reading the parade video scope is similar to that of the waveform. However, you now look at the balance between the colors correct the white balance, and check for a color cast.
The Parade works almost in a similar manner as the waveform. It displays the red, green, and blue channels of the image as separate waveforms. This way, you can easily identify and correct color casts while ensuring the colors in the image are balanced. The video scope provides useful information to decide which parts of the image need to be corrected or tweaked further.
3. Vectorscope
Vectorscope in DaVinci Resolve shows hue and saturation on a circular graph. Hues (the colors) are indicated outside of the color wheel for easier color correction. Saturation is indicated by how far the graph extends from the center.
By displaying the hue and saturation of the image as a vector, this video scope helps check skin tones. The scope specifically checks whether skin tones are shifted toward colors such as yellow, magenta, or green. It allows you to make sure that the colors in your subject skin tones are not too saturated or desaturated.
4. Histogram
Histogram is a video scope in DaVinci Resolve that displays the brightness or luminance of an image from left to right for the RGB channel. The video scope is based on the number of pixels that the colors red, blue, and green have in an image.
Using the histogram video scope on DaVinci Resolve allows you to check for overexposure or underexposure in your image. You can also ensure that the image has a good overall brightness range. The scope provides a graphical representation of tonal distribution in each channel. This way, you can evaluate the tone in detail for more accurate brightness and contrast adjustments.
Part 3: Edit Like a Pro: Mastering Video Scopes in Filmora
When working on video projects, Wondershare Filmora is a great editing software. It comes with unique features to color-correct your videos on the go as you edit it. From AI-powered features to royalty-free music, there is so much more you can do with Filmora.
Free Download For Win 7 or later(64-bit)
Free Download For macOS 10.14 or later
How to Use Video Scopes on Filmora
Using video scopes on Filmora is easy. The software offers four video scope options, allowing you to color-correct and grade your visual images properly. They include parade RGB, waveform, vectorscope, and histogram. When editing videos on Filmora, the video scopes can be accessed by clicking on the video scopes icon. The icon is found on the top right corner of the media player.
Filmora has made it easy for users to manage video scopes, and color-correct videos quickly. Users can change the layout options of the video scopes to match the editing needs of their project. You can also expand the button to show the name of the scope. As you manage the scopes, you can start with the Parade to make the necessary adjustments. Then move on to waveform, vectorscope, and histogram.
The uses of the video scope on Filmora are as follows:
- Parade – Cahnge the color channel from RBG to YRGB or YCbCr
- Vectorscope – Identify skin tone
- Waveform – Adjust color channels in a different way
- Histogram – Display the multiple color adjustments in a graphical way
Conclusion
Scopes are indeed valuable to video editors and colorists. While viewing images on a monitor can be subjective, scopes allow you to analyze and define them objectively. This gives you the power to color grade and correct to ensure that viewers look at the image with a clear representation. When working on or editing your videos, we recommend Wondershare Filmora. The video editing software comes with a wide range of features and video scopes that allow you to do everything on the same platform.
Free Download Use Vectorscope in Filmora Try Color Correction

Part 1. Unlocking Color Precision: Exploring the Improved Scopes in DaVinci Resolve
The Blackmagic Design continues to improve the Resolve to make it better with every iteration. The new features improve colorist workflow in less powerful ways. The major improvements include a major facelift to the scope, allowing professions to do more with DaVinci resolve. Let’s have a look at some of these changes:
1. CIE 1931 Color Space
The inclusion of the CIE chromaticity diagram is perhaps the biggest change to DaVinci scopes. It displays the gamut of the project as set in the Color Management preferences. This makes it a useful alternate way of looking at the trace of an image to judge when the values are out of legal range. It also functions as an educational tool for learning about the range of color spaces.
2. Low Pass Filter
The wavefront and parade scopes now have a low pass filter, which reduces noise in the trace. This visually sharpens the display of the scopes, allowing easier detection of elements in the frame.
The image above shows the major improvements. The second set of waveforms has more defined lines. These have the low-pass filter activated, which makes the scopes easier to read.
3. High, Mid, and Low Views in Vectorscope
The vectorscope has been added to the ability to toggle the mid-tones, shadows, and highlights of the image independently. You can set the ranges with greater visualization control.
As seen in the picture above, the vectorscope controls allow you to select the low, mid, or high range of the image. You can also set the low and high ranges as desired.
4. Histograms Over Curves
Another great DaVinci scope is the histogram, which now appears outside of the scope panel. The new improvements have embedded the histogram inside the Curves tab on the bottom Palette. Click on the three dots in the Custom Curves tab. The pulldown menu that appears includes the Input or Output of the histogram. With these settings, you can find the element in the frame that helps you make adjustments quickly.
5. Scope Quality
The GPU-accelerated scopes engine allows the scopes to respond quickly. Users have the option to set the quality to high, medium, or low and the scopes will respond to a range of hardware systems. Depending on whether you are working on a stationary short or looking to see how the scopes react in real-time, you will be able to toggle the modes quickly and easily.

6. YRGB View in Histogram and Parade
The histogram and parade now come with the ability to view luminance together with the red, green, and blue channels. Users also have the option for YCbCr mode in the Parade.

7. Extents
These are weak elements in the signore, which are of lesser importance compared to the stronger elements. However, Danvici now allows them to be revealed for a full illustration of the information that lies in the image. Consequently, extents can be used to determine whether the data is being clipped beyond legal limits.

Part 2. Mastering Scopes in DaVinci Resolve: A Brief Guide
DaVinci scopes help you to analyze images as a basis for color correction. When used properly, scopes help in fixing white balance issues and checking saturation. They also allow you to get the correct exposure and check details like skin tone. To use scopes in DaVinci Resolve, go to the color page in the bottom right corner. You can also click on the small graph icon to view the scope. Here is how to use them:
1. Waveform
The Waveform represents the brightness or luminance of your image. In this video scope, the brightest parts are at the top while the darkest are at the bottom. The pixels are represented from left to right.
The Waveform scope on DaVinci Resolve is helpful when you are checking for clipping. This simply means finding out whether the image is too bright or too dark. The waveform also ensures that the image is properly exposed. The colorize feature of the waveform shows the colors of the image while the extent shows the darkest or lightest parts of the image.
2. Parade (RGB)
The RGB Parade comprises 3 waveforms that represent the luminance of red, green, and blue channels. The approach for reading the parade video scope is similar to that of the waveform. However, you now look at the balance between the colors correct the white balance, and check for a color cast.
The Parade works almost in a similar manner as the waveform. It displays the red, green, and blue channels of the image as separate waveforms. This way, you can easily identify and correct color casts while ensuring the colors in the image are balanced. The video scope provides useful information to decide which parts of the image need to be corrected or tweaked further.
3. Vectorscope
Vectorscope in DaVinci Resolve shows hue and saturation on a circular graph. Hues (the colors) are indicated outside of the color wheel for easier color correction. Saturation is indicated by how far the graph extends from the center.
By displaying the hue and saturation of the image as a vector, this video scope helps check skin tones. The scope specifically checks whether skin tones are shifted toward colors such as yellow, magenta, or green. It allows you to make sure that the colors in your subject skin tones are not too saturated or desaturated.
4. Histogram
Histogram is a video scope in DaVinci Resolve that displays the brightness or luminance of an image from left to right for the RGB channel. The video scope is based on the number of pixels that the colors red, blue, and green have in an image.
Using the histogram video scope on DaVinci Resolve allows you to check for overexposure or underexposure in your image. You can also ensure that the image has a good overall brightness range. The scope provides a graphical representation of tonal distribution in each channel. This way, you can evaluate the tone in detail for more accurate brightness and contrast adjustments.
Part 3: Edit Like a Pro: Mastering Video Scopes in Filmora
When working on video projects, Wondershare Filmora is a great editing software. It comes with unique features to color-correct your videos on the go as you edit it. From AI-powered features to royalty-free music, there is so much more you can do with Filmora.
Free Download For Win 7 or later(64-bit)
Free Download For macOS 10.14 or later
How to Use Video Scopes on Filmora
Using video scopes on Filmora is easy. The software offers four video scope options, allowing you to color-correct and grade your visual images properly. They include parade RGB, waveform, vectorscope, and histogram. When editing videos on Filmora, the video scopes can be accessed by clicking on the video scopes icon. The icon is found on the top right corner of the media player.
Filmora has made it easy for users to manage video scopes, and color-correct videos quickly. Users can change the layout options of the video scopes to match the editing needs of their project. You can also expand the button to show the name of the scope. As you manage the scopes, you can start with the Parade to make the necessary adjustments. Then move on to waveform, vectorscope, and histogram.
The uses of the video scope on Filmora are as follows:
- Parade – Cahnge the color channel from RBG to YRGB or YCbCr
- Vectorscope – Identify skin tone
- Waveform – Adjust color channels in a different way
- Histogram – Display the multiple color adjustments in a graphical way
Conclusion
Scopes are indeed valuable to video editors and colorists. While viewing images on a monitor can be subjective, scopes allow you to analyze and define them objectively. This gives you the power to color grade and correct to ensure that viewers look at the image with a clear representation. When working on or editing your videos, we recommend Wondershare Filmora. The video editing software comes with a wide range of features and video scopes that allow you to do everything on the same platform.
Everything You Need to Know About Color Grading in Photography
Create High-Quality Video - Wondershare Filmora
An easy and powerful YouTube video editor
Numerous video and audio effects to choose from
Detailed tutorials provided by the official channel
Have you recognized how flat your images look when you take them with your camera? While the scenery may be beautiful and your photography skills may be amazing, there’s always something missing. That “thing” is color grading, and that may be why your favorite superstar’s pictures appear better than yours. You can color grade your videos to produce the same effect too.
Color grading photography refers to a post-production process that improves your images by altering their color. The result of an excellent color grading process is an image that looks more appealing and refined. It’s what gives a picture some professional touch.
If you want to learn more about color grading photography, this article will let you in on all you need to know. From essential color grading steps to terms, tools, etc., you can begin your journey to cool and exciting images after reading.
In this article
01 Don’t Confuse Color Grading With Color Correction
03 Common Steps To Color Grade a Photo
04 Tips For Color Grading Photography
Don’t Confuse Color Grading With Color Correction
The first way to fully appreciate color grading is by differentiating it from its closest term—color correction. Many people use both of them interchangeably, and that’s wrong. Although color grading and color correction are post-production processes that enhance image colors, they perform different roles.
Here’s how to differentiate color grading from color correction:
| Differentiating Factor | Color Grading ; | Color Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Color grading is a process that enhances an image’s color by stylizing or giving it a cinematic appearance. | Color correction is a process that adjusts color mistakes in an image by giving it a consistent appearance. This process balances colors by adjusting whites and blacks. |
| Purpose | The primary aim of color grading an image is to evoke specific emotions in the viewers. Color grading leverages the emotional and psychological effects of colors to manipulate the viewers’ moods. You can use color grading to give your images different tones or themes like fear, femininity, youthfulness, passion, anger, sadness, etc. | Unlike color grading, the color correction does very little in setting the tone or mood that an image carries. Instead, it corrects specific mistakes in the image to make it look as natural to the human eyes as possible. Generally, camera lenses and the human eyes view pictures differently. Color correction changes a photo’s look to make it more appealing to humans than the camera. It makes black colors appear darker and adds more white to whites to create the desired effect. |
| Stage in the production process | Color grading typically comes after color correction in the post-production process. That’s because the effects of color grading are more appealing on a color-corrected picture. | Color correction comes before color grading. This process does the major work of balancing colors and correcting errors. Color grading only fine-tunes what color correction has done, giving it a professional finish. |
| Example | One of the most obvious examples of color grading is in motion pictures. For example, Sci-Fi movies typically have a very saturated blue color. However, you will notice a little redder in romantic movies. Note that filmmakers can use different color grades in movies to draw attention to specific details or represent changes in the storyline. Color grading produces the same effects in pictures. | Color correction is most prominent in documentaries to make pictures and videos look more real to the human eye. Other times, color corrections just adjust one color to merge the rest of the image or video. |

Terms and Tools Used In Color Grading
These are the most common terminologies photo editors use when color grading an image:
● Hue
Hue is the general name for describing pure color. That means it defines color without alluding to its brightness, vividness, etc. It describes a color’s position in the color wheel.
● Saturation
When a photo editor talks about saturation, they refer to the hue concentration that defines a specific color. Saturation describes color shades and focuses on how colorful they are. Examples of colors with zero saturation are white, black, and grey.
● Luminance
Luminous describes how bright, well-lighted or dark a color is. Highlights, mids, and shadows can influence luminance.

● Additive Color
Additive colors are non-primary colors. However, they typically result from mixing primary colors (blue, red, green).
● Color Cast
Color cast means that the image’s coloring doesn’t look as natural as it should be. This usually happens when different light sources get mixed.
● Temperature
Temperature defines how cool or warm a color is. Cool temperatures typically describe blues and purples, while orange and red represent the warmth.
The essential tools for color grading include
● White Balance
White balance helps to make your photos look more natural by correcting color cast issues. After using white balance, the result is that the whites in your pictures would look exactly like the human eye will perceive it. White balance adjusts your image’s color cast to make them look warmer or cooler.
● Brightness and Contrast
Brightness and contrast are essential in color grading and are among the most used photo editing tools. Different sliders control brightness and contrast during editing. It’s important to note that your image’s brightness will affect the contrast and vice-versa. That’s why they usually appear together, even if they refer to different tools.
● The Three-Way Color Corrector
Many photographers refer to the three-way corrector as the color correction’s workhorse. That’s because this tool adjusts hue, saturation, brightness, and contrast in a single interface. The three-way corrector performs the job of three tools in one interface. Using the three-way corrector ensures that you work faster than usual.
● The Fast Color Corrector
The fast color corrector is like the three-way corrector. However, there are many limitations with the number of potential looks you can achieve with this tool. The fast color corrector primarily focuses on adjusting tint and saturation. Its major advantage over the three-way corrector is its user-friendliness and simplicity.
● Curves
While using curves is pretty complicated, the tool offers impressive functionality that you can’t refuse. Curves are very powerful and precise. Their main function is to overhaul or remove your image’s brightness altogether to give it a distinctive look.
● The Unsharp Mask and Sharpening Tools
With the unsharp mask and sharpening tools, you can give your picture’s edges a sharp illusion by modifying the contrast. This is typically useful for images that you shoot in dark conditions.
Sharp pictures are always a lovely sight. However, these tools can’t correct pictures taken out of focus. To get the best results from these tools. Then you can start moving them back till you get your desired sharpness.
● Color Match
As the make implies, color match tools modify a target picture’s colors to fit the reference image. This is an automatic process and helps to save time.
Common Steps To Color Grade a Photo
These are the essential stages for color grading your images:
● Step 1:
The first step in color grading is deciding how warm or cool you want your image to look. Then, modify the white balance to suit your desired warmth or coolness.
● Step 2:
After adjusting the white balance, the next step is to adjust saturation or hue.
● Step 3:
The next step is to focus on the histogram. A histogram is a common feature in many photo editing software that informs you of your image’s tonal values. The goal in this stage is to ensure equal color distribution. Keep adjusting your image till the colors are even.
● Step 4:
Work on your highlights and shadows by modifying the green, red, and blue curves. Also, adjust your vibrancy setting for a good effect.
● Step 5:
Explore split toning. Split toning is a process that involves adding colors to highlight and shadows independently. Learning how to split tone can make a difference in your photo editing.
Tips For Color Grading Photography
The following best practices will enhance your color grading:
- About oversaturation or under-saturation. Your saturation should be just right to produce the perfect result. So, always be sure to pay maximum attention to this process. This tip is particularly useful when working with portraits.
- Remember that color grading doesn’t fix a bad shot. So, be sure to improve your photography skills and take the best shots for excellent color grading results.
- Shoot your images in RAW. Doing this guarantees more control over your pictures’ colors.
- Always experiment with different looks until you get your precise effect. Lightroom is one of the best color grading apps to use.
- Exercise maximum caution when manipulating backgrounds. Don’t do too much, especially when you’re taking an indoor shot. That’s because manipulating indoor backgrounds too much can mismatch the foreground and background, making your portrait look weird.
Conclusion
● While your photography skills are essential in influencing your image’s outcome; your color grading skills will take it to another level. It’s one of the fastest ways to make a budding photo editor look like a pro.
● After reading this article, you can be sure that you have the basic information you need to achieve your editing goals. However, you mustn’t stop here. Continuous learning, especially through constant practice, is the way to go. You can visit Filmora today for the best color grading packages and tools.
Have you recognized how flat your images look when you take them with your camera? While the scenery may be beautiful and your photography skills may be amazing, there’s always something missing. That “thing” is color grading, and that may be why your favorite superstar’s pictures appear better than yours. You can color grade your videos to produce the same effect too.
Color grading photography refers to a post-production process that improves your images by altering their color. The result of an excellent color grading process is an image that looks more appealing and refined. It’s what gives a picture some professional touch.
If you want to learn more about color grading photography, this article will let you in on all you need to know. From essential color grading steps to terms, tools, etc., you can begin your journey to cool and exciting images after reading.
In this article
01 Don’t Confuse Color Grading With Color Correction
03 Common Steps To Color Grade a Photo
04 Tips For Color Grading Photography
Don’t Confuse Color Grading With Color Correction
The first way to fully appreciate color grading is by differentiating it from its closest term—color correction. Many people use both of them interchangeably, and that’s wrong. Although color grading and color correction are post-production processes that enhance image colors, they perform different roles.
Here’s how to differentiate color grading from color correction:
| Differentiating Factor | Color Grading ; | Color Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Color grading is a process that enhances an image’s color by stylizing or giving it a cinematic appearance. | Color correction is a process that adjusts color mistakes in an image by giving it a consistent appearance. This process balances colors by adjusting whites and blacks. |
| Purpose | The primary aim of color grading an image is to evoke specific emotions in the viewers. Color grading leverages the emotional and psychological effects of colors to manipulate the viewers’ moods. You can use color grading to give your images different tones or themes like fear, femininity, youthfulness, passion, anger, sadness, etc. | Unlike color grading, the color correction does very little in setting the tone or mood that an image carries. Instead, it corrects specific mistakes in the image to make it look as natural to the human eyes as possible. Generally, camera lenses and the human eyes view pictures differently. Color correction changes a photo’s look to make it more appealing to humans than the camera. It makes black colors appear darker and adds more white to whites to create the desired effect. |
| Stage in the production process | Color grading typically comes after color correction in the post-production process. That’s because the effects of color grading are more appealing on a color-corrected picture. | Color correction comes before color grading. This process does the major work of balancing colors and correcting errors. Color grading only fine-tunes what color correction has done, giving it a professional finish. |
| Example | One of the most obvious examples of color grading is in motion pictures. For example, Sci-Fi movies typically have a very saturated blue color. However, you will notice a little redder in romantic movies. Note that filmmakers can use different color grades in movies to draw attention to specific details or represent changes in the storyline. Color grading produces the same effects in pictures. | Color correction is most prominent in documentaries to make pictures and videos look more real to the human eye. Other times, color corrections just adjust one color to merge the rest of the image or video. |

Terms and Tools Used In Color Grading
These are the most common terminologies photo editors use when color grading an image:
● Hue
Hue is the general name for describing pure color. That means it defines color without alluding to its brightness, vividness, etc. It describes a color’s position in the color wheel.
● Saturation
When a photo editor talks about saturation, they refer to the hue concentration that defines a specific color. Saturation describes color shades and focuses on how colorful they are. Examples of colors with zero saturation are white, black, and grey.

● Luminance
Luminous describes how bright, well-lighted or dark a color is. Highlights, mids, and shadows can influence luminance.

● Additive Color
Additive colors are non-primary colors. However, they typically result from mixing primary colors (blue, red, green).
● Color Cast
Color cast means that the image’s coloring doesn’t look as natural as it should be. This usually happens when different light sources get mixed.
● Temperature
Temperature defines how cool or warm a color is. Cool temperatures typically describe blues and purples, while orange and red represent the warmth.
The essential tools for color grading include
● White Balance
White balance helps to make your photos look more natural by correcting color cast issues. After using white balance, the result is that the whites in your pictures would look exactly like the human eye will perceive it. White balance adjusts your image’s color cast to make them look warmer or cooler.
● Brightness and Contrast
Brightness and contrast are essential in color grading and are among the most used photo editing tools. Different sliders control brightness and contrast during editing. It’s important to note that your image’s brightness will affect the contrast and vice-versa. That’s why they usually appear together, even if they refer to different tools.
● The Three-Way Color Corrector
Many photographers refer to the three-way corrector as the color correction’s workhorse. That’s because this tool adjusts hue, saturation, brightness, and contrast in a single interface. The three-way corrector performs the job of three tools in one interface. Using the three-way corrector ensures that you work faster than usual.
● The Fast Color Corrector
The fast color corrector is like the three-way corrector. However, there are many limitations with the number of potential looks you can achieve with this tool. The fast color corrector primarily focuses on adjusting tint and saturation. Its major advantage over the three-way corrector is its user-friendliness and simplicity.
● Curves
While using curves is pretty complicated, the tool offers impressive functionality that you can’t refuse. Curves are very powerful and precise. Their main function is to overhaul or remove your image’s brightness altogether to give it a distinctive look.
● The Unsharp Mask and Sharpening Tools
With the unsharp mask and sharpening tools, you can give your picture’s edges a sharp illusion by modifying the contrast. This is typically useful for images that you shoot in dark conditions.
Sharp pictures are always a lovely sight. However, these tools can’t correct pictures taken out of focus. To get the best results from these tools. Then you can start moving them back till you get your desired sharpness.
● Color Match
As the make implies, color match tools modify a target picture’s colors to fit the reference image. This is an automatic process and helps to save time.
Common Steps To Color Grade a Photo
These are the essential stages for color grading your images:
● Step 1:
The first step in color grading is deciding how warm or cool you want your image to look. Then, modify the white balance to suit your desired warmth or coolness.
● Step 2:
After adjusting the white balance, the next step is to adjust saturation or hue.
● Step 3:
The next step is to focus on the histogram. A histogram is a common feature in many photo editing software that informs you of your image’s tonal values. The goal in this stage is to ensure equal color distribution. Keep adjusting your image till the colors are even.
● Step 4:
Work on your highlights and shadows by modifying the green, red, and blue curves. Also, adjust your vibrancy setting for a good effect.
● Step 5:
Explore split toning. Split toning is a process that involves adding colors to highlight and shadows independently. Learning how to split tone can make a difference in your photo editing.
Tips For Color Grading Photography
The following best practices will enhance your color grading:
- About oversaturation or under-saturation. Your saturation should be just right to produce the perfect result. So, always be sure to pay maximum attention to this process. This tip is particularly useful when working with portraits.
- Remember that color grading doesn’t fix a bad shot. So, be sure to improve your photography skills and take the best shots for excellent color grading results.
- Shoot your images in RAW. Doing this guarantees more control over your pictures’ colors.
- Always experiment with different looks until you get your precise effect. Lightroom is one of the best color grading apps to use.
- Exercise maximum caution when manipulating backgrounds. Don’t do too much, especially when you’re taking an indoor shot. That’s because manipulating indoor backgrounds too much can mismatch the foreground and background, making your portrait look weird.
Conclusion
● While your photography skills are essential in influencing your image’s outcome; your color grading skills will take it to another level. It’s one of the fastest ways to make a budding photo editor look like a pro.
● After reading this article, you can be sure that you have the basic information you need to achieve your editing goals. However, you mustn’t stop here. Continuous learning, especially through constant practice, is the way to go. You can visit Filmora today for the best color grading packages and tools.
Have you recognized how flat your images look when you take them with your camera? While the scenery may be beautiful and your photography skills may be amazing, there’s always something missing. That “thing” is color grading, and that may be why your favorite superstar’s pictures appear better than yours. You can color grade your videos to produce the same effect too.
Color grading photography refers to a post-production process that improves your images by altering their color. The result of an excellent color grading process is an image that looks more appealing and refined. It’s what gives a picture some professional touch.
If you want to learn more about color grading photography, this article will let you in on all you need to know. From essential color grading steps to terms, tools, etc., you can begin your journey to cool and exciting images after reading.
In this article
01 Don’t Confuse Color Grading With Color Correction
03 Common Steps To Color Grade a Photo
04 Tips For Color Grading Photography
Don’t Confuse Color Grading With Color Correction
The first way to fully appreciate color grading is by differentiating it from its closest term—color correction. Many people use both of them interchangeably, and that’s wrong. Although color grading and color correction are post-production processes that enhance image colors, they perform different roles.
Here’s how to differentiate color grading from color correction:
| Differentiating Factor | Color Grading ; | Color Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Color grading is a process that enhances an image’s color by stylizing or giving it a cinematic appearance. | Color correction is a process that adjusts color mistakes in an image by giving it a consistent appearance. This process balances colors by adjusting whites and blacks. |
| Purpose | The primary aim of color grading an image is to evoke specific emotions in the viewers. Color grading leverages the emotional and psychological effects of colors to manipulate the viewers’ moods. You can use color grading to give your images different tones or themes like fear, femininity, youthfulness, passion, anger, sadness, etc. | Unlike color grading, the color correction does very little in setting the tone or mood that an image carries. Instead, it corrects specific mistakes in the image to make it look as natural to the human eyes as possible. Generally, camera lenses and the human eyes view pictures differently. Color correction changes a photo’s look to make it more appealing to humans than the camera. It makes black colors appear darker and adds more white to whites to create the desired effect. |
| Stage in the production process | Color grading typically comes after color correction in the post-production process. That’s because the effects of color grading are more appealing on a color-corrected picture. | Color correction comes before color grading. This process does the major work of balancing colors and correcting errors. Color grading only fine-tunes what color correction has done, giving it a professional finish. |
| Example | One of the most obvious examples of color grading is in motion pictures. For example, Sci-Fi movies typically have a very saturated blue color. However, you will notice a little redder in romantic movies. Note that filmmakers can use different color grades in movies to draw attention to specific details or represent changes in the storyline. Color grading produces the same effects in pictures. | Color correction is most prominent in documentaries to make pictures and videos look more real to the human eye. Other times, color corrections just adjust one color to merge the rest of the image or video. |

Terms and Tools Used In Color Grading
These are the most common terminologies photo editors use when color grading an image:
● Hue
Hue is the general name for describing pure color. That means it defines color without alluding to its brightness, vividness, etc. It describes a color’s position in the color wheel.
● Saturation
When a photo editor talks about saturation, they refer to the hue concentration that defines a specific color. Saturation describes color shades and focuses on how colorful they are. Examples of colors with zero saturation are white, black, and grey.

● Luminance
Luminous describes how bright, well-lighted or dark a color is. Highlights, mids, and shadows can influence luminance.

● Additive Color
Additive colors are non-primary colors. However, they typically result from mixing primary colors (blue, red, green).
● Color Cast
Color cast means that the image’s coloring doesn’t look as natural as it should be. This usually happens when different light sources get mixed.
● Temperature
Temperature defines how cool or warm a color is. Cool temperatures typically describe blues and purples, while orange and red represent the warmth.
The essential tools for color grading include
● White Balance
White balance helps to make your photos look more natural by correcting color cast issues. After using white balance, the result is that the whites in your pictures would look exactly like the human eye will perceive it. White balance adjusts your image’s color cast to make them look warmer or cooler.
● Brightness and Contrast
Brightness and contrast are essential in color grading and are among the most used photo editing tools. Different sliders control brightness and contrast during editing. It’s important to note that your image’s brightness will affect the contrast and vice-versa. That’s why they usually appear together, even if they refer to different tools.
● The Three-Way Color Corrector
Many photographers refer to the three-way corrector as the color correction’s workhorse. That’s because this tool adjusts hue, saturation, brightness, and contrast in a single interface. The three-way corrector performs the job of three tools in one interface. Using the three-way corrector ensures that you work faster than usual.
● The Fast Color Corrector
The fast color corrector is like the three-way corrector. However, there are many limitations with the number of potential looks you can achieve with this tool. The fast color corrector primarily focuses on adjusting tint and saturation. Its major advantage over the three-way corrector is its user-friendliness and simplicity.
● Curves
While using curves is pretty complicated, the tool offers impressive functionality that you can’t refuse. Curves are very powerful and precise. Their main function is to overhaul or remove your image’s brightness altogether to give it a distinctive look.
● The Unsharp Mask and Sharpening Tools
With the unsharp mask and sharpening tools, you can give your picture’s edges a sharp illusion by modifying the contrast. This is typically useful for images that you shoot in dark conditions.
Sharp pictures are always a lovely sight. However, these tools can’t correct pictures taken out of focus. To get the best results from these tools. Then you can start moving them back till you get your desired sharpness.
● Color Match
As the make implies, color match tools modify a target picture’s colors to fit the reference image. This is an automatic process and helps to save time.
Common Steps To Color Grade a Photo
These are the essential stages for color grading your images:
● Step 1:
The first step in color grading is deciding how warm or cool you want your image to look. Then, modify the white balance to suit your desired warmth or coolness.
● Step 2:
After adjusting the white balance, the next step is to adjust saturation or hue.
● Step 3:
The next step is to focus on the histogram. A histogram is a common feature in many photo editing software that informs you of your image’s tonal values. The goal in this stage is to ensure equal color distribution. Keep adjusting your image till the colors are even.
● Step 4:
Work on your highlights and shadows by modifying the green, red, and blue curves. Also, adjust your vibrancy setting for a good effect.
● Step 5:
Explore split toning. Split toning is a process that involves adding colors to highlight and shadows independently. Learning how to split tone can make a difference in your photo editing.
Tips For Color Grading Photography
The following best practices will enhance your color grading:
- About oversaturation or under-saturation. Your saturation should be just right to produce the perfect result. So, always be sure to pay maximum attention to this process. This tip is particularly useful when working with portraits.
- Remember that color grading doesn’t fix a bad shot. So, be sure to improve your photography skills and take the best shots for excellent color grading results.
- Shoot your images in RAW. Doing this guarantees more control over your pictures’ colors.
- Always experiment with different looks until you get your precise effect. Lightroom is one of the best color grading apps to use.
- Exercise maximum caution when manipulating backgrounds. Don’t do too much, especially when you’re taking an indoor shot. That’s because manipulating indoor backgrounds too much can mismatch the foreground and background, making your portrait look weird.
Conclusion
● While your photography skills are essential in influencing your image’s outcome; your color grading skills will take it to another level. It’s one of the fastest ways to make a budding photo editor look like a pro.
● After reading this article, you can be sure that you have the basic information you need to achieve your editing goals. However, you mustn’t stop here. Continuous learning, especially through constant practice, is the way to go. You can visit Filmora today for the best color grading packages and tools.
Have you recognized how flat your images look when you take them with your camera? While the scenery may be beautiful and your photography skills may be amazing, there’s always something missing. That “thing” is color grading, and that may be why your favorite superstar’s pictures appear better than yours. You can color grade your videos to produce the same effect too.
Color grading photography refers to a post-production process that improves your images by altering their color. The result of an excellent color grading process is an image that looks more appealing and refined. It’s what gives a picture some professional touch.
If you want to learn more about color grading photography, this article will let you in on all you need to know. From essential color grading steps to terms, tools, etc., you can begin your journey to cool and exciting images after reading.
In this article
01 Don’t Confuse Color Grading With Color Correction
03 Common Steps To Color Grade a Photo
04 Tips For Color Grading Photography
Don’t Confuse Color Grading With Color Correction
The first way to fully appreciate color grading is by differentiating it from its closest term—color correction. Many people use both of them interchangeably, and that’s wrong. Although color grading and color correction are post-production processes that enhance image colors, they perform different roles.
Here’s how to differentiate color grading from color correction:
| Differentiating Factor | Color Grading ; | Color Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Color grading is a process that enhances an image’s color by stylizing or giving it a cinematic appearance. | Color correction is a process that adjusts color mistakes in an image by giving it a consistent appearance. This process balances colors by adjusting whites and blacks. |
| Purpose | The primary aim of color grading an image is to evoke specific emotions in the viewers. Color grading leverages the emotional and psychological effects of colors to manipulate the viewers’ moods. You can use color grading to give your images different tones or themes like fear, femininity, youthfulness, passion, anger, sadness, etc. | Unlike color grading, the color correction does very little in setting the tone or mood that an image carries. Instead, it corrects specific mistakes in the image to make it look as natural to the human eyes as possible. Generally, camera lenses and the human eyes view pictures differently. Color correction changes a photo’s look to make it more appealing to humans than the camera. It makes black colors appear darker and adds more white to whites to create the desired effect. |
| Stage in the production process | Color grading typically comes after color correction in the post-production process. That’s because the effects of color grading are more appealing on a color-corrected picture. | Color correction comes before color grading. This process does the major work of balancing colors and correcting errors. Color grading only fine-tunes what color correction has done, giving it a professional finish. |
| Example | One of the most obvious examples of color grading is in motion pictures. For example, Sci-Fi movies typically have a very saturated blue color. However, you will notice a little redder in romantic movies. Note that filmmakers can use different color grades in movies to draw attention to specific details or represent changes in the storyline. Color grading produces the same effects in pictures. | Color correction is most prominent in documentaries to make pictures and videos look more real to the human eye. Other times, color corrections just adjust one color to merge the rest of the image or video. |

Terms and Tools Used In Color Grading
These are the most common terminologies photo editors use when color grading an image:
● Hue
Hue is the general name for describing pure color. That means it defines color without alluding to its brightness, vividness, etc. It describes a color’s position in the color wheel.
● Saturation
When a photo editor talks about saturation, they refer to the hue concentration that defines a specific color. Saturation describes color shades and focuses on how colorful they are. Examples of colors with zero saturation are white, black, and grey.

● Luminance
Luminous describes how bright, well-lighted or dark a color is. Highlights, mids, and shadows can influence luminance.

● Additive Color
Additive colors are non-primary colors. However, they typically result from mixing primary colors (blue, red, green).
● Color Cast
Color cast means that the image’s coloring doesn’t look as natural as it should be. This usually happens when different light sources get mixed.
● Temperature
Temperature defines how cool or warm a color is. Cool temperatures typically describe blues and purples, while orange and red represent the warmth.
The essential tools for color grading include
● White Balance
White balance helps to make your photos look more natural by correcting color cast issues. After using white balance, the result is that the whites in your pictures would look exactly like the human eye will perceive it. White balance adjusts your image’s color cast to make them look warmer or cooler.
● Brightness and Contrast
Brightness and contrast are essential in color grading and are among the most used photo editing tools. Different sliders control brightness and contrast during editing. It’s important to note that your image’s brightness will affect the contrast and vice-versa. That’s why they usually appear together, even if they refer to different tools.
● The Three-Way Color Corrector
Many photographers refer to the three-way corrector as the color correction’s workhorse. That’s because this tool adjusts hue, saturation, brightness, and contrast in a single interface. The three-way corrector performs the job of three tools in one interface. Using the three-way corrector ensures that you work faster than usual.
● The Fast Color Corrector
The fast color corrector is like the three-way corrector. However, there are many limitations with the number of potential looks you can achieve with this tool. The fast color corrector primarily focuses on adjusting tint and saturation. Its major advantage over the three-way corrector is its user-friendliness and simplicity.
● Curves
While using curves is pretty complicated, the tool offers impressive functionality that you can’t refuse. Curves are very powerful and precise. Their main function is to overhaul or remove your image’s brightness altogether to give it a distinctive look.
● The Unsharp Mask and Sharpening Tools
With the unsharp mask and sharpening tools, you can give your picture’s edges a sharp illusion by modifying the contrast. This is typically useful for images that you shoot in dark conditions.
Sharp pictures are always a lovely sight. However, these tools can’t correct pictures taken out of focus. To get the best results from these tools. Then you can start moving them back till you get your desired sharpness.
● Color Match
As the make implies, color match tools modify a target picture’s colors to fit the reference image. This is an automatic process and helps to save time.
Common Steps To Color Grade a Photo
These are the essential stages for color grading your images:
● Step 1:
The first step in color grading is deciding how warm or cool you want your image to look. Then, modify the white balance to suit your desired warmth or coolness.
● Step 2:
After adjusting the white balance, the next step is to adjust saturation or hue.
● Step 3:
The next step is to focus on the histogram. A histogram is a common feature in many photo editing software that informs you of your image’s tonal values. The goal in this stage is to ensure equal color distribution. Keep adjusting your image till the colors are even.
● Step 4:
Work on your highlights and shadows by modifying the green, red, and blue curves. Also, adjust your vibrancy setting for a good effect.
● Step 5:
Explore split toning. Split toning is a process that involves adding colors to highlight and shadows independently. Learning how to split tone can make a difference in your photo editing.
Tips For Color Grading Photography
The following best practices will enhance your color grading:
- About oversaturation or under-saturation. Your saturation should be just right to produce the perfect result. So, always be sure to pay maximum attention to this process. This tip is particularly useful when working with portraits.
- Remember that color grading doesn’t fix a bad shot. So, be sure to improve your photography skills and take the best shots for excellent color grading results.
- Shoot your images in RAW. Doing this guarantees more control over your pictures’ colors.
- Always experiment with different looks until you get your precise effect. Lightroom is one of the best color grading apps to use.
- Exercise maximum caution when manipulating backgrounds. Don’t do too much, especially when you’re taking an indoor shot. That’s because manipulating indoor backgrounds too much can mismatch the foreground and background, making your portrait look weird.
Conclusion
● While your photography skills are essential in influencing your image’s outcome; your color grading skills will take it to another level. It’s one of the fastest ways to make a budding photo editor look like a pro.
● After reading this article, you can be sure that you have the basic information you need to achieve your editing goals. However, you mustn’t stop here. Continuous learning, especially through constant practice, is the way to go. You can visit Filmora today for the best color grading packages and tools.
Also read:
- Updated Best Ways to Add Photos to Tik Tok Video
- Progressive Solutions to Adding VHS Effects to Video with Ease
- Instagram Doesnt Offer Native Support for GIF Files. So, in This Post, Well Learn How to Convert a GIF to a Video for Instagram Using Multiple Methods. For 2024
- New A Review of Efectum App Making Slow Motion Video
- New In 2024, 3 Actionable Ways to Create Countdown Animation for Videos
- In 2024, Steps to Denoise in Final Cut Pro – Reduce Video and Audio Noise
- New 2024 Approved How To Add Fade In Windows Video Editor
- Updated In 2024, 2 Methods to Crop Video in VLC
- New In 2024, Elevate Your Designs with Feather Shapes in After Effects
- New How to Create Photoshop GIF The 100 Easy Way for 2024
- Updated In 2024, How to Create Your Own LUTs for Your Video with Filmora
- In 2024, Split Audio From Video in Adobe Premiere Pro Step by Step
- In 2024, Designed for You! Best Image (JPG/PNG) to GIF Converters
- 2024 Approved Camtasia Vs. Final Cut Pro
- Updated In 2024, Camtasia Review – Is It The Best Video Editor?
- Updated 2024 Approved How to Make Glitch Effect with Filmora
- New In 2024, How to Trim/Crop Video in Microsoft Powerpoint
- New Unraveling How the Slow Motion Guys Have Revolutionized The Slow Motion Game for 2024
- How to Use Canva Color Match for 2024
- Updated The Complete Guide to Converting GIF to SVG With Ease for 2024
- Updated Everything That You Need to Know About Video Montages- Ideas, Techniques, and Software
- Detailed Guide to Crop Video in Sony Vegas Pro
- In 2024, Best 10 iPad Slideshow Apps to Create a Slideshow
- Updated End This Problem! Make Transparent Background Video Today for 2024
- New Best CapCut Templates for Slow Motion Video Trend
- Take Your Video Editing to the Next Level with Video Scopes for 2024
- New Dubbing Videos With Voiceovers | Using Wondershare Filmora
- Final Cut Pro for iPad
- What Is the Best MP4 Cutter for YouTuber on Mac for 2024
- In 2024, Understanding The Best Tools for Changing Sky Background
- Updated How to Create Video in Text Intro, In 2024
- New If You Want an App to Make Videos with Pictures and Music for Social Media Posts, We Are with the Best Apps to Make Videos with Music and Pictures
- Frame Blending Is a Great Way to Smooth Out Your Video Footage in Adobe Premiere Pro. Using This Technique, You Can Create a More Natural Looking Motion by Averaging Out the Frames in Your Clips
- New Splitting the Clips in Adobe After Effects Step by Step for 2024
- Updated 2024 Approved Easy Step by Step Tutorial on Creating a Lightroom Collage
- Updated Have You Ever Used Premiere Pro to Create Slow-Motion Effects? This Article Will Provide a Guide on Producing Slow-Motion Effects by Using Adobe Premiere Pro
- New 2024 Approved Create Intro Video with Flixpress
- New Top List Best VHS Sound Effect That You Can Use in Video Making for 2024
- New Do You Know How to Create AI Thumbnails for Videos? This Article Will Mention some of the Best Tools to Generate Attractive Thumbnails for Videos with AI
- New Tactics to Make Transparent Image in Minimal Steps
- Do You Want to Apply LUTs Using Open Broadcaster Software? You Can Download Free LUTs for OBS and Apply Them to Your Files. There Are Many LUTs Available
- Updated In 2024, Best 20 Slideshow Makers for Win/Mac/Online Review
- Updated Making Slow Motion Videos in Premiere Pro A Review on The Best Method
- New How to Color-Correct an S-Log Footage
- Updated Guide To Cropping and Combining Content in Wondershare Filmora Latest for 2024
- Updated Brighten a Video in Windows 10 Easily When Video Clips You Recorded on Your Windows 10 Computer or Those Downloaded From YouTube Are Too Dark or Too Bright, You Can Easily Adjust the Color Levels in a Few Clicks
- 2024 Approved Magic Effects Video Making How To
- Disabling iPhone 12 Pro Parental Restrictions With/Without Password | Dr.fone
- In 2024, How to Fix Pokemon Go Route Not Working On Nokia XR21? | Dr.fone
- Reasons for Vivo Y78+ Stuck on Boot Screen and Ways To Fix Them | Dr.fone
- How To Remove Screen Lock PIN On Realme V30 Like A Pro 5 Easy Ways
- Remove FRP Lock on Yuva 2 Pro
- How To Fix Unresponsive Phone Touchscreen Of Samsung Galaxy S23+ | Dr.fone
- In 2024, How to Come up With the Best Pokemon Team On Motorola Edge 40 Pro? | Dr.fone
- The Ultimate Guide to Get the Rare Candy on Pokemon Go Fire Red On Motorola Edge 2023 | Dr.fone
- In 2024, What Does Jailbreaking Apple iPhone 11 Pro i Do? Get Answers here
- Pattern Locks Are Unsafe Secure Your Realme 12+ 5G Phone Now with These Tips
- How to Change Spotify Location After Moving to Another Country On Vivo Y78+ (T1) Edition | Dr.fone
- Can I Bypass a Forgotten Phone Password Of Xiaomi Redmi 13C?
- In 2024, Top 15 Augmented Reality Games Like Pokémon GO To Play On Realme Narzo 60 5G | Dr.fone
- In 2024, How Can We Unlock Our Realme C33 2023 Phone Screen?
- In 2024, Best 3 Software to Transfer Files to/from Your Motorola Edge 40 Neo via a USB Cable | Dr.fone
- In 2024, Where Is the Best Place to Catch Dratini On Poco C55 | Dr.fone
- Which is the Best Fake GPS Joystick App On Nubia Z50 Ultra? | Dr.fone
- In 2024, Top 15 Augmented Reality Games Like Pokémon GO To Play On Realme 12 Pro+ 5G | Dr.fone
- In 2024, How Can We Bypass Xiaomi Redmi Note 12R FRP?
- In 2024, Top 10 Fingerprint Lock Apps to Lock Your Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra Phone
- In 2024, 5 Ways To Teach You To Transfer Files from Motorola Moto G23 to Other Android Devices Easily | Dr.fone
- Reasons for Oppo Reno 11 5G Stuck on Startup Screen and Ways To Fix Them | Dr.fone
- Title: New Have You Ever Used the Path Blur Effect in Your Photos? This Article Will Address How to Use Path Blur in Photoshop to Generate Appealing Results Accurately
- Author: Chloe
- Created at : 2024-04-24 07:08:19
- Updated at : 2024-04-25 07:08:19
- Link: https://ai-editing-video.techidaily.com/new-have-you-ever-used-the-path-blur-effect-in-your-photos-this-article-will-address-how-to-use-path-blur-in-photoshop-to-generate-appealing-results-accurat/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.











